What is coupling?
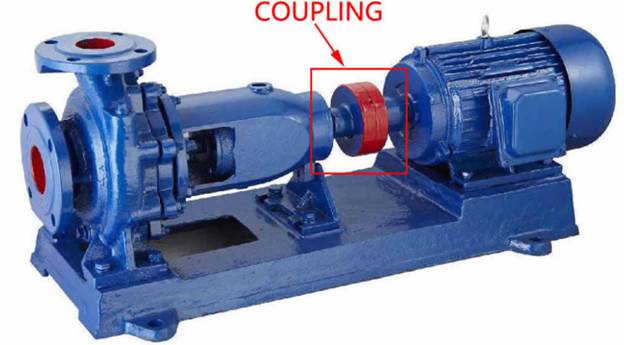
A coupling is a mechanical element that transmits torque/power from one shaft to another. In pumps, couplings connect the prime mover shaft to the pump shaft to allow power/torque transmission while allowing some misalignment to prevent shaft failure. The coupling rotate at the same speed as the shaft it is connected to. Also, coupling in pumps helps absorb vibrations from the prime mover (diesel engine or electric motor) and protects the pump. Centrifugal pump manufacturers design the coupling to not transfer heat from the prime mover side to the pump. Allowing heat into the pump may cause damage to the mechanical seals and thus cause leakage.
Figure: A centrifugal pump and its coupling.
Causes of Coupling Failure in Pumps
Misalignment
Misalignment occurs due to improper pump and motor installation, pipe strain, and bent shafts. There are three main types of misalignment: angular, parallel misalignment and combined misalignment.
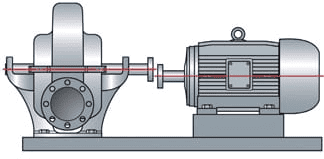
Parallel misalignment is caused by two shafts that have their rotational axes parallel and not perfectly aligned. One of the symptoms of this misalignment is uneven loads on bearings and, thus, increased noise and vibrations. As such, the bearings wears out rapidly. It also causes excess heat on the shafts and seals.
Figure: Parallel misalignment.
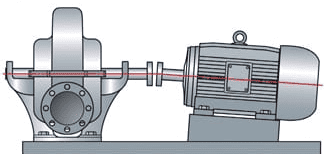
Angular misalignment happens when two shafts/couplings are not connected at the same angle. It causes the shafts/couplings to intersect at a certain angle, as shown below. This misalignment results in high axial loads and excess vibrations, leading to premature wear on seals, and bearings.
Figure: Angular misalignment.
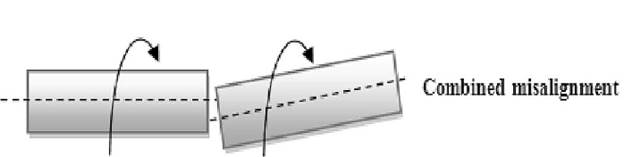
Combined misalignment occurs when the coupling suffers from both angular and parallel misalignment. It is the most common of the three misalignments. It causes several problems in centrifugal pumps, such as rapid wear and tear on bearings, and seals. It also leads to low efficiency and severe pump damage. Also, due to misalignment the pump flow rate reduces while consuming a lot of power.
Figure: Combined misalignment.
Inadequate Lubrication
Some couplings, such as grid and gear couplings, need sufficient Lubrication. Check the lubricant level as recommended by the centrifugal pump manufacturer and flush it out to remove foreign materials that may aid in premature failure.
Poor coupling selection
Delivery and cost are among the main factors when selecting a coupling for your pump. However, if it is chosen wrongly, it might have severe consequences, such as damage to the pump and motor, and also cause injury during operation. Other vital factors to consider when selecting pump coupling are misalignment, available space, backlash, windup, torque, stiffness, inertia, environmental factors, shaft mounting, and ease of maintenance. Also, it is recommended to select a coupling with good dampening capability to reduce vibration and shock.
Poor maintenance
Lack of correct regular maintenance causes premature failure on couplings. Perform preventive maintenance to avoid premature failure. Such maintenance practices include scheduled visual inspections to check for signs of fatigue and wear. Also, performing regular cleaning aids reduces failure. Also, lubricate the couplings according to the centrifugal pump manufacturer’s instructions to prevent wear and overheating.
Torque capacity
There are different types and sizes of pump couplings. Each of the couplings is designed for a specific torque limit. It has been found that 10 to 15% of coupling failures are due to exceeding the torque limit. Excess torque damages the coupling, pump, motor, and pumping system. Consult pump experts to help you determine the correct coupling for your intended pumping needs.
Environmental causes
Coupling damage could also be due to harmful chemicals and extreme temperatures (cold or hot). Fluids like acids may corrode couplings, thus reducing their mechanical strength. Temperature changes may cause thermal expansion, leading to misalignment and premature failure.
Manufacturing and metallurgical defects
Though rare, coupling could fail due to metallurgical and manufacturing flaws. Such defects could be due to defective materials, poor production methods, and incorrect design considerations.
How to prevent pump coupling failure
- Ensure shafts and couplings are correctly aligned. Dial indicators and laser methods are the two good methods for checking alignment.
- Prevent harmful chemicals and heavy equipment from falling on the pump and coupling.
- Ensure proper installation. Follow the instructions given by the centrifugal pump manufacturer when installing/assembling the pump.
- Perform regular visual inspection to check alignment, lubrication, and fatigue on the coupling.
- Avoid excess loads on the pump. Exceeding the coupling/shaft torque limit will cause severe damage even to the pump.
- Clean the couplings and remove foreign materials.
- Store them in a clean, dry place to prevent chemical attack and deterioration.
Symptoms of a failing centrifugal pump coupling
- Excess noise and vibrations.
- Excess shaft vibrations and wobbling.
- Failed mechanical seals leading to fluid leakage.
- Low pump efficiency.
- Excessive power consumption.
- Overheating.
- Damaged bearings and seals.
- Cracked coupling.