Submersible Borehole Pump
What is a submersible borehole pump?
A submersible borehole pump is a pump that must be constantly submerged in a borehole and is powered using a submersible motor. It is a typical centrifugal pump because it converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy using the centrifugal force acting on the liquid. The pump’s motor is usually rigidly coupled to the pump head and can be located on top or underneath the pump, depending on the application. A submersible borehole pump is designed with a smaller diameter and long axial length to fit in typical borehole conditions. Depending on the pump requirements, the various pump components can be constructed from cast iron, alloy steel, or plastic. Submersible borehole pumps mainly apply to pumping borehole water for drinking, irrigation, or firefighting water. Submersible borehole pump manufacturers avail the units in single-stage and multistage designs. A submersible borehole pump is highly cost-effective, especially for great installation depths, because it’s raising main has a compact design.

Figure: showing the configuration of a submersible borehole pump
Components of a submersible borehole pump
Electric motor
The submersible borehole pump employs a squirrel-cage motor that is close-coupled and hermetically sealed to prevent water from leaking into it and causing damage. The electric motor is the source of mechanical power in a submersible borehole pump. Submersible borehole pump manufacturers also fit the pump with a built-in protection device, which helps to shut down the pump in case of any challenge.
Pump casing
The casing is the outside shell of the pump. It features a sealed construction to retain pressure and protect against leakage. The pump casing houses the impeller, shaft, bearing housing, and other internal components. It also directs the pumped liquid into and out of the pump through the delivery pipe. Submersible borehole pump manufacturers differentiate pump casings mainly by design, and the pump casing can be either radially split or axially split. Depending on the application requirements, the pump casing can be manufactured from cast iron, alloy steel, or plastic.
Shaft
The shaft is the part of the rotor supporting the impeller and riding on bearings. Submersible borehole water pump manufacturers make the shaft from stainless steel and carbon steel materials to overcome vibrations and heavy loads during pump operations.
Impeller
The impeller comprises an arrangement of backward-curved vanes and rides on the electric motor’s shaft. It displaces fluid through the pump by increasing its kinetic energy and pressure. The impeller can be open, semi-open, or closed type.
Bearings
The primary purpose of the bearings is to support the shaft or the impeller and to align them correctly with the fixed ends under the action of radial and axial forces. They also help to reduce the friction between the rotating shaft and the stator and contain the relative motion of the rotor assembly.
Electrical cable
The purpose of the electrical cable is to deliver power to the submersible borehole pump. Submersible pumps for dirty water can have two or three power cables depending on the motor design.
Delivery Pipe
The primary purpose of the delivery pipe is to lift fluid to the required area. The delivery pipe has two ends, with one end connecting to the outlet of the pump and the other delivering the water to a needed destination.
Valves
The submersible borehole pump also contains different valves that help to operate the pump. Such valves include relief valves, drain valves, and ball valves.
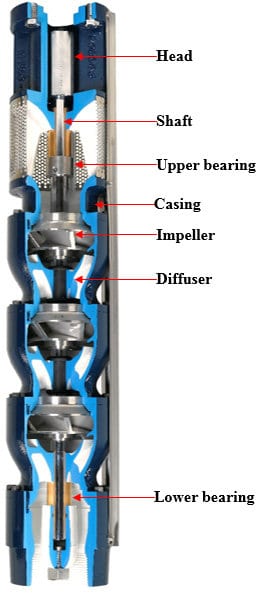
Figure: Components of a submersible borehole pump
How does a submersible borehole pump work?
The submersible borehole pump pushes water from great depths to a storage tank on the surface. The pump’s operation involves converting energy from electrical into mechanical and then kinetic and pressure energy of the fluid. When the motor starts, the pump impeller rotates the water inside the pump’s casing, imparting high kinetic energy to the liquid. The impeller then throws the water into the volute, where the increased fluid velocity is converted into high static pressure as the fluid speed decreases due to the gradually enlarging flow path. The resulting high-pressure head helps to push the liquid to the surface and transport it to the designated location via the delivery connections.
Types of submersible borehole pumps
Single-stage submersible borehole pump
A single-stage submersible borehole pump consists of one impeller rotating on a shaft in a pump chamber, designed to pressurize and push the liquid to the surface when powered using a motor. It is the most straightforward design of the submersible borehole pump, therefore cheaper and easy to acquire. However, it produces less power compared to multistage pump.
Figure 1: Single-stage submersible borehole pump.
Multistage submersible borehole pump
Multistage submersible borehole pump consists of more than two impellers housed in different pump chambers mounted in series or chain-like design. The transfer liquid is drawn into the first chamber (stage) at suction pressure and exits from the last chamber at elevated pressure. A multistage submersible borehole pump can manage superior pressure ranges and flow rates than the single-stage counterpart. A multistage submersible borehole pump can also generate greater power and static pressure using a smaller motor, thereby consuming less energy.
Figure 1: Multistage submersible borehole pump.
Applications of a submersible borehole pump
The principal applications of submersible borehole pumps include irrigation, construction pits, underground mining, municipal water supply, and geothermal power plants. Their typical uses include the following:
- They are used for pumping borehole water or underground water from great depths into storage tanks.
- They are used in deep-well drilling and offshore drilling rigs.
- They are used for supplying water in firefighting applications.
- They are used for pumping tasks in the municipal water supply.
- They are also used in geothermal energy and deep-sea mining.
- They are also used for dewatering mines.
- They are used to clear construction pits.
Advantages of a submersible borehole pump
- A submersible borehole pump prevents cavitation in the pump’s components because it eliminates the spike in fluid pressure as the fluid flows through the pump.
- Submersible borehole pumps use less energy because they rely on atmospheric pressure to draw fluid without a suction line. Therefore, unlike suction pumps, submersible borehole pumps do not spend any energy to draw fluid into the pump.
- They are made of corrosion-resistant material and have a long service life.
- A submersible borehole pump is more efficient and reliable in pumping water from deep underground than other pumps.
- They have a robust construction that is easy to install and operate.
- They have minimal maintenance requirements.
- They are self-priming. A submersible borehole pump operates below the water surface, and the user is not required to prime the pump before regular operation manually.
- They are quiet in operation since they sit in the pumped liquid.
- They are excellent for large quantities of water and a wide range of flow rates.
- The submersible borehole pump manufacturers can match the pump to handle water containing significant suspended solid particles.
- A submersible borehole pump has minimal risk of overheating because the pumped liquid surrounds it, helping to cool the pump’s motor.
Disadvantages of a submersible borehole pump
- Submersible borehole pumps are located at great depths below the surface and can be difficult to access for repairs and maintenance. This challenge can make the pump operate for a long time without regular inspection.
- The pump must be submerged in the transfer medium to prevent overheating. Running dry can damage the unit.
- The pump seals may corrode over an extended duration of pump operation, causing pump leakage.
- The use of mechanical seals also makes the pump’s motor challenging to disassemble for repairs.
- Submersible borehole pumps are more complex and expensive than shallow-well pumps.
Troubleshooting a submersible borehole pump
The motor does not run
- There is a broken power cable in the submersible borehole pump. Inspect and change the power cable if necessary.
- There is no power supply to the Control Panel. Use a voltmeter to check the mains input to the panel. Ensure the power cable connections follows the submersible borehole pump manufacturer’s manual.
- There is heavy sedimentation around the pump. Inspect the submersible pump and remove any build-up.
- There is a tripped circuit breaker or blown-out fuse. Reset the circuit breaker if necessary. Inspect the pump for a blown-out fuse and replace it.
- There are shortcomings in the motor wiring. Consult a licensed electrical technician to inspect the conditions of the pump wiring and repair any faults.
The pump gives little or no discharge at all.
- The pump is operating in reverse. Be sure to reverse the motor polarities. Check that the motor rotation direction follows the submersible borehole pump manufacturer’s guide.
- The discharge pipe is blocked. Inspect and clean the discharge pipe.
- The impeller is dirty or clogged. Clean the pump inside, and remove any dirt or blocking material from the impeller.
- The pump’s discharge head is insufficient. Ensure that the pump’s discharge head is in line with the system design values provided by the submersible borehole pump manufacturer.
Thermal trip
- The pump head is too low. Adjust the pump head or install a control valve to detect back pressure according to the set value.
- The stop level is too low. Verify the stop switch level from the submersible borehole pump manufacturer’s manual and make necessary adjustments.
- The liquid density or viscosity is too high. Ensure that the pump matches the application. Also, make sure all the valves are open.
- The driver is overloaded. Ensure the pump is drawing the correct amount of current according to the submersible pump specifications.
Low pump flow rate
- There is excessive clearance leading to fluid recirculation. Ensure that the impeller is of the correct size following the submersible borehole pump manufacturer’s guide.
- The impeller is severely worn-out. Inspect the impeller for wear and replace it if necessary.
- The pump’s motor is rotating in reverse. Reverse the motor polarities.
- The discharge pipe is blocked. Inspect and clear any blockage from the discharge pipe.
- The suction is clogged. Clear the suction from any debris.
The leakage detector is activated
- The detector cable is compromised by wear, damage, or contact with oils. Inspect the detector cable and replace it.
The pump is overheating
- There is an issue with the electrical system. Inspect the wiring and connections to ensure all components are tight and secure. Also, inspect the pump’s power consumption to verify if it is as per the submersible borehole pump manufacturer’s details.
- There is a heavy build-up of organic or mineral material outside the motor. Inspect and clean any build-up from the engine.
- The thermostat is set too high. Reset the thermostat to the temperature level specified by the submersible borehole pump manufacturers.
- There are problems with the cooling system, e.g., a low cooling water flow rate. Ensure that the cooling system is working correctly and that there are no leaks.
- The bearings are severely worn-out. Inspect the bearings and replace them as needed.
Summary
A submersible borehole pump is a type of centrifugal pump that must be constantly submerged in the water to be extracted and uses a submersible motor. It converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy using the centrifugal force acting on the pumped liquid. The pump’s motor is usually close-coupled to the pump head and hermetically sealed. Depending on the application demand, the submersible borehole pump can feature cast iron, stainless steel, alloy steel, or plastic construction. Submersible borehole pumps mainly apply to pumping borehole water from great depths to storage tanks on the surface for different uses. Submersible borehole pump manufacturers tailor the unit to have a smaller diameter and long axial length to fit in typical boreholes. Submersible borehole pump manufacturers offer the pumps in single-stage and multistage designs. They provide numerous benefits, including compact design, minimal maintenance requirements, high energy efficiency, reliability, and quiet operation.


