Splitting Sewage Pump
What is a splitting sewage pump?
A splitting sewage pump is a type of pump for moving fluid containing a high percentage of hard solids and fabulous matters. It is designed with a tearing mechanism to tear and cut-off fabulous materials such as long fibers, bags, grass, cloth strips, and the like in the sewage before being discharged. Splitting sewage pump manufacturers design this pump to move very dirty, viscous, and slippery liquids from one place to another. It falls under a category of sewage pumps known as grinder pumps. Like a waste grinder, grinder pumps slice and grove solid elements in the pumping sewage. Splitting sewage manufacturers mostly design the pump from cast iron because it is affordable, long-lasting, and can resist corrosion in the harsh sewage environment. A splitting sewage pump offers excellent performance capabilities with a flow rate of up to 200 cubic meters per hour, a maximum head of 30 meters, a wide range of pumping speeds (from 1450 to 2900 revolutions per minute), and the ability to handle sewage at different temperatures (between-15 and 60 degrees centigrade).
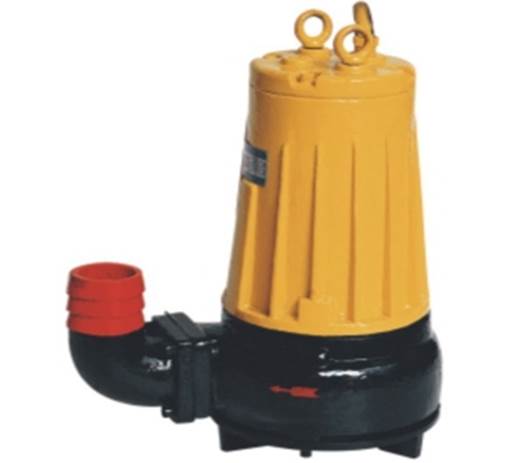

Figure: Splitting sewage pump
The pump is submersible meaning it is fully immersed in the sewage to be transported to a maximum depth of five 5 meters. It also has a close coupled design a single, continuous shaft between the motor and pump, rather than 2 shafts coupled. Splitting sewage pump is extensively used in different industries including urban sewage treatment plants and chemical plants. It is also a key component of municipal engineering and facilities for handling sewage and feculence-containing particles. Splitting sewage pump features a compact design and is easily portable because it does not require setting up a pump room. It is also versatile and can move sewage reliably and efficiently.
Components of a splitting Sewage pump
Electric motor
The motor provides the mechanical power to run the pump impeller. It is the drive that converts the electrical energy supply into mechanical energy to rotate the pump impeller. The electric motor consists of a rotor, stator, commutator, and shaft sleeve. It also has two types of windings: stator and rotor windings. The motor winding is wires placed within coils and enclosed in coated soft iron magnetic core to produce magnetic poles when the current flow in them. Electric motors can be powered using AC or DC. DC derives from batteries while AC comes from power grids, generators, and inverters.
Close coupling
A splitting sewage pump consists of a close coupling between the motor and the rotor. The purpose of the coupling is to transmit torque from the motor to the rotor assembly. In a close coupling, the impeller is directly mounted on the motor shaft and the pump casing is bolted to the drive end of the motor, instead of being installed on a pump bearing frame. A close coupling is simple to design and it does not need alignment, or a separate base plate since it comprises only a single shaft.
Volute (casing)
The volute is the curved casing that receives the fluid. It houses the pump’s internal complement. Including the impeller and shaft. It also features a suction inlet where the water enters and a discharge outlet from which the water exits. The volute also directs the fluid out of the pump through the delivery pipe. When the pumping fluid enters the volute, its flow rate decreases while the pressure increases. The volute is also sealed to prevent leakage and retain pressure
Impeller
The impeller is the component containing a series of backward-curved vanes and is usually placed inside the volute and mounted on the pump shaft. Its function is to increase both the kinetic energy and pressure of the fluid. As the impeller rotates, it transfers the kinetic energy derived from a source, i.e., an electric motor, to the fluid, thereby increasing the fluid pressure and inducing fluid flow. The impeller design is a significant factor in determining the pump’s efficiency. Splitting sewage pump manufacturers produce two types of impellers have two types: Axial flow impeller and Radial flow impeller. The fluid flows axially to the pump shaft in axial impellers, while in a radial impeller, the fluid moves perpendicularly to the post. Axial impellers primarily apply for high-flow and low-pressure applications. On the other hand, radial impellers find use in multistage split-case centrifugal pumps.
Mechanical seals
The purpose of mechanical seals is to reduce leakage between the rotating shaft and the stationary pump casing. Two seal faces or surfaces maintain contact at a sealing interface. One seal face rotates with the shaft while the other one is stationary. Mechanical seals in a splitting sewage pump consist of four main components: the first face, second pages, actuation, and the drive i.e., the motor. The primary seal face rotates with the pump shaft and is embedded in the pump casing. It is usually made from tungsten carbide, silicon carbide, or ceramics. The second face is normally stationary. The mechanical seal sits inside the seal cover plate with the stationary surface pressing against the cover plate and the other one rotating with the shaft. This configuration creates a watertight barrier that prevents leakage through the motor.
Motor capacitor
The motor capacitor stores electrical energy and releases it to the copper windings, creating an extra boost and increasing the motor torque. The splitting sewage pump manufacturers specify a motor capacitor based on several parameters such as capacitance, physical size, voltage rating, frequency, and operating temperature.
Suction inlet and discharge outlet
The fluid enters the splitting sewage pump through the suction inlet and exits through the discharge outlet.
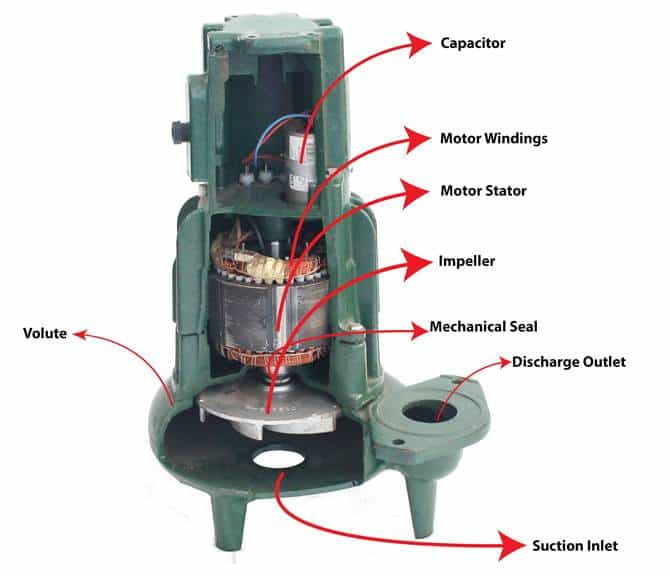
Figure: Showing various components of a splitting sewage pump
How does a splitting sewage pump work?
When the pump is turned on, the motor rotates the impeller, which creates a vacuum inside the pump due to the centrifugal effect. As a result, the liquid is drawn into the impeller’s eye through the suction grid fitted to the bottom of the pump. As the impeller rotates the tearing mechanism slices and cuts off any fibrous material in the fluid. The swirling flow then enters the volute where the fluid flow speed gradually decreases leading to the conversion of the high-velocity energy into high-pressure energy. Finally, the volute directs the fluid under high pressure into the discharge outlet where it leaves the pumps and moves to the desired location through the discharge pipes.
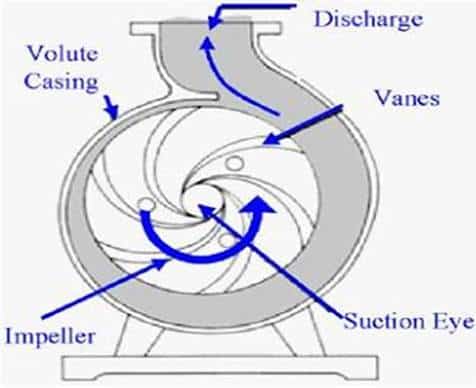
Figure: Working of a splitting sewage pump
Types of splitting Sewage pumps
Single suction splitting Sewage pumps
In this pump, the fluid enters the pump impeller from one side. It has a simple design and is cheaper than the double suction.
Figure: Showing a single-suction splitting sewage pump.
Double suction splitting Sewage pumps
In this kind of pump, the impeller is designed to draw fluid from either side. The double suction design eliminates axial forces on the impeller and can manage higher flow than the single suction design. it is also less vulnerable to the wear and tear caused by axial thrust, which occurs when fluid enters the impeller
Figure: Showing a double-suction splitting sewage pump
Applications of a splitting Sewage pump
Splitting sewage pumps are extensively used in many industries, including urban sewage treatment, chemical, and paper making. Typical uses include the following:
- Splitting sewage pumps are used for handling sewage and feculence-containing particles in public facilities and municipal engineering
- They are used in wastewater drainage in factories, construction sites, and commercial facilities.
- They are used in the drainage system in municipal sewage treatment plants.
- They are used in drainage stations in residential quarters.
- They are core components of most Municipal projects.
- They are perfect for methane pools and field irrigation in the countryside.
Advantages of a splitting Sewage pump
- Splitting sewage pump has simple and cost-effective construction
- It is easy to install and maintain
- It has a high blow down capacity
- It can run without blocking due to the non-blockage tearing mechanism
- It can easily handle the solid and fibrous matter in sewage without damage
- The close-coupled design of the motor and pump enhances the pump’s portability
- It is highly energy efficient and reliable in operation
- The pump can operate without cavitation
- It is convenient and easy to operate
- It is self-priming; doesn’t have to be primed before the operation
Disadvantages of a splitting Sewage pump
- Splitting sewage pump cannot run dry and must always be immersed in the fluid
- It may not completely drain a surface in automatic mode because it must be immersed
- Unnoticeable wear and tear may occur leading to leakage and motor corrosion
Troubleshooting a splitting Sewage pump
The motor does not start
- The motor is wrongly wired. Ensure that the power cables are connected according to the splitting sewage pump manufacturer’s guide.
- The motor is damaged. Disassemble the motor and inspect the windings and internal connections. If there are burn marks the motor is likely blown out and needs to be replaced.
- The centrifugal fuse or capacitor has failed. Inspect the fuse or capacitor and replace it
- The fuse is blown out or the circuit breaker is tripped. Inspect the pump for a blown fuse and replace it. Reset the circuit breaker if necessary.
- The pump cables are broken. Inspect and change the cables if necessary.
Zero pump discharge
- The pump does not fill with the liquid before starting. Unblock the suction inlet.
- The impeller is clogged. Clean the impeller to remove any blockage.
- The pump is operating in reverse. Reverse the motor polarities. Check that the motor rotation direction follows the splitting sewage pump manufacturer’s guide.
- The discharge pipe is blocked. Disassemble the discharge connection, inspect it and remove any blockage.
The Pump provides an unstable flow
- The voltage is too low, causing the pump speed to decrease. Inspect the voltage supply and adjust it as necessary.
- The bottom valve is leaking. Inspect the bottom valve for leakage and correct or replace it if necessary.
- The impeller or seal ring is severely worn-out. Inspect the impeller or seal ring for wear and replace them if you find it fit.
The pump capacity is low
- There is a blockage in the discharge hose. Inspect and clear any blockage from the discharge hose.
- The pump is reversed. Reverse pump polarities
- The pump casing or impeller is partially clogged. Inspect and clean the pump inside.
- The impeller is worn out. Inspect the impeller for wear and replace it if necessary.
The pump does not develop pressure
- Leakage in the mechanical seals. Inspect and replace mechanical seals if it is necessary
- The discharge line is closed and priming air can’t find the way out. Open the discharge line
- The pump cannot self-prime. Ensure that the suction inlet is not blocked and the fluid can enter the pump
- Leakage in the foot valve or check valve. Inspect and replace the valves.
Summary
A splitting sewage pump is used for moving fluid containing high percentages of hard solid and fabulous matter. It features a tearing mechanism that slices and cuts-off fabulous materials such as long fibers, bags, grass, cloth strips, and the like in the sewage before they can be discharged. Splitting sewage pump manufacturers design the pump with a close coupled design where the motor is directly bolted to the pump without a supporting flame. The close-coupled design minimizes manufacturing costs and enhances the pump’s portability and ease of operation. During operation, the pump is completely immersed in the pumping liquid and can go as deep as 5 meters. Splitting sewage pump excellently caters to different industries including urban sewage treatment plants, chemical plants, and paper making. This kind of pump is used for handling sewage and feculence-containing particles in public facilities and municipal engineering. It is also perfect for transferring very dirty, viscous, and slippery liquids from one place to another.


