Oil Transfer Vortex Impeller Pump
What is Oil Transfer Vortex Impeller Pump?
This is a pump used for transferring oil and fuel products and other related substances from one point to another. This type of pump is mostly used in servicing heavy equipment and truck fleets with lubricants and fuel. The pump removes liquids from the source like tanks, located above or below the ground level. Oil transfer vortex impeller pump manufacturers design this pump to operate using impellers that create a vacuum inside the pump to help force the liquid from its source like a tank into the pump. The impeller then imparts energy into the fluid making it able to move through the pump into the discharge section and then into the pipeline for transportation. As the name suggests, this pump uses a vortex type of impeller suitable for use in different media including those that contain solids and debris since it can create a whirlpool to keep solids away from the impeller as the liquid moves through, thus keeping internal parts against damage.

Figure: Oil transfer vortex impeller pump.
Components of an oil transfer vortex impeller pump
Motor
This is the component that provides power needed to transfer the liquid. The motor is powered by electricity from the mains supply. It works by converting that electricity to mechanical energy and outputs it as torque and speed through a shaft.
Motor shaft
This is the component of the oil transfer vortex impeller pump that connects the motor to the pump. This shaft is used to transmit power from the motor to the pump. Oil transfer vortex impeller pump manufacturers machine this shaft from strong metallic materials such as carbon steel and stainless steel to make sure it has high strength to transmit the torque needed to operate the pump.
Vortex impeller
This is the component used create a pressure difference between the interior of the pump and the surface of the liquid. The impeller is powered by the motor through its shaft so that both can rotate at the same high speed. The impeller also helps to impart kinetic energy to the liquid so that it can move faster.
Casing
This is the housing or shell that protects and supports other components of the pump. It is used to enhance fluid pressure while reducing its velocity. It is designed with high strength materials to withstand high fluid pressure and temperature as well as prevent fluid leakage.
Suction pipe
This is a pipe connected to the inlet port of the pump. It is used to convey liquid from its source into the pump. This pipe is also attached to the suction valve that controls the flow of fluid into the pump. A strainer is also mounted to help filter out unwanted materials getting into the pump.
Discharge pipe and valve
Discharge pipe connects the pump to the pipeline. It is used to convey the fluid from the pump into the piping system. This pipe is also connected to the discharge valve that regulates the amount of fluid leaving the pump into the pipeline.
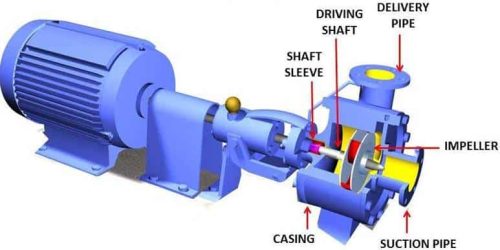
Figure: Components of oil transfer vortex impeller pump.
How does oil transfer vortex impeller pump work?
This pump operates by rotating its impeller at a very high speed. The power to run the impeller is provided by the motor through its shaft. When the pump is turned on, the motor shaft starts spinning at high rpm. The motor shaft is connected to the pump shaft to transmit power. The vortex impeller is mounted on the pump shaft. As such, the pump shaft rotates at the same speed as the motor forcing the impeller to rotate and create a vacuum in the pump. The vacuum means that the pressure inside the pump is lower than the atmospheric pressure. As such, the pressure on the surface of the fluid forces the liquid into the pump due to the pressure difference. When the liquid enters the pump, the impeller imparts velocity on it. The fluid proceeds to the casing where its velocity is reduced while its pressure energy is increased. The high-pressure energy is responsible for moving the liquid to the required point.
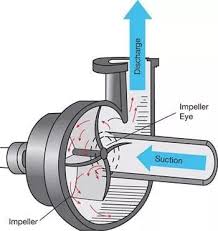
Figure: Working of an oil transfer vortex impeller pump
Types of oil transfer vortex impeller pump
Magnetic drive oil transfer vortex impeller pump
This is a pump that employs magnetic technology to transmit power from the motor to the pump shaft. This technology uses two magnetic rings. One of the magnets is the outer (drive) magnet and the other one is the inner (driven) magnet. The two magnets are arranged with their poles opposite to enhance the magnetic field pattern. The outer magnet is connected to the motor while the inner magnet is connected to the impeller shaft. As such, when the motor is turned on, the drive magnet spins and due to the magnetic field pattern, the inner magnet starts rotating. Rotation of the inner magnet creates rotary motion on the impeller.
This type of oil transfer vortex impeller pump is best for transporting liquids that are free from solids. Solids stick on the magnet thus lowering pump performance or damaging the pump. However, if this pump is used according to the guidelines given by the oil transfer vortex impeller pump manufacturer, it lasts for a long period since there are no mechanical seals that can wear out rapidly. This type of pump is best for transporting liquids that are hazardous since it is designed to be leak-proof. Such design properties save you from legal action which happens with other pumps that leak hazardous fluids.
Figure: Magnetic drive oil transfer vortex impeller pump.
Self-priming oil transfer vortex impeller pump
This is a pump that is able of removing air before it starts normal pumping operation. The pump operates by first creating a partial vacuum to discharge liquid while also removing air. During the priming process, the liquid and air are combined. This forces the air to rise and the liquid sinks or goes down. Due to gravity, the liquid is in the impeller and mixes with air remaining in the suction line. The process keeps repeating until all the air is removed and a vacuum is created on the suction line. Then atmospheric pressure forces the liquid into the suction line and to the impeller allowing the pumping process to start.
Figure: Self-priming oil transfer vortex impeller pump.
Multistage oil transfer vortex impeller pump
This is a pump designed with more than two impellers connected in series. As such, this pump has multiple fluid chambers connected in series. Each chamber has one impeller, a diffuser, and a return guide vane, and all of them are housed in the casing. The impellers are mounted on one shaft and driven by power from the motor. This design allows the liquid to flow through the chambers in a linear direction. After the pump is primed, the liquid enters the suction line and flows into the first stage or chamber. It then passes through the various impellers sequentially from the first one to the last one. By flowing through all the chambers, the liquid leaves the pump at very high pressure. Each impeller feeds the next impeller, and as such, pressure increases further. Oil transfer vortex impeller pump manufacturers design this pump such that, the more the number of chambers, the more the final outlet pressure. However, despite the pressure increasing at every stage, the flow range remains constant for the given motor speed.
Figure: Multistage oil transfer vortex impeller pump.
Single-stage oil transfer vortex impeller pump
This is a pump designed with one impeller hence the name “single-stage”. This is one of the most common types of oil transfer vortex impeller pumps. The impeller rotates on a shaft housed by the pump casing. Rotation of the impeller causes fluid to flow through the pump. It is of simple and compact design, with lightweight and cheaper relative to the multistage pump.
Applications of oil transfer vortex impeller pump
- It is used in the transfer of cutting oil.
- An oil transfer vortex impeller pump is used in the transportation of heavy crude oil.
- These pumps are used in drilling mud/fluid needed in petroleum engineering to perform rock cutting, lubrication, and cooling of the drill bit.
- It is used to transfer diesel fuel and heavy oil.
- It transports gasoline and kerosene.
- It is used to transport black water.
- It is used in multiphase fluid transfer.
- Oil transfer vortex impeller pumps are used in the transportation of oil and wax mixture.
- They are used in oil sludge, waste, and skimming applications.
- They are used in off-shore oil transfer.
- These pumps are used in polymer flooding and polymer transfer.
Advantages of oil transfer vortex impeller pump
- These pumps are of simple and compact design.
- Oil transfer vortex impeller pumps are of different sizes allowing their use in areas with small and large spaces.
- They are versatile as they can be used to transfer different types of media.
- They are easy to install, repair and maintain if used according to the guidelines given by the oil transfer vortex impeller pump manufacturer.
- They are energy efficient as they have less friction compared to other pumps like gear pumps.
- They have smooth flow as they do not have pulsating fluid flow.
- Oil transfer vortex impeller pumps are reliable.
- They are resistant to corrosion.
Disadvantages of API610 BB1 double suction petrochemical pumps
- These pumps are large and heavy in weight. They need cranes to be lifted during installation.
- They are expensive relative to other pumps.
- They are prone to cavitation especially when the NPSH is too low.
- They consume a lot of energy due to the large impeller and shafts used to make the pump.
Disadvantages of oil transfer vortex impeller pump
- These pumps tend to suffer from cavitation.
- They need to be primed.
Troubleshooting oil transfer vortex impeller pump
There is no fluid flow through the pump
- The pump is not primed. Prime the pump and ensure the suction line and pump are full of liquid.
- Blockage on the suction line. Remove the blocking material.
- Clogged impeller. Open the pump and remove any clogging material.
- Wrong motor rotation. Change the direction of motor rotation as indicated by an arrow on the pump casing.
- Suction valve is closed. Open the suction valve.
- High suction lift. Reduce the suction lift by reducing the suction pipe and moving the pump closer to the source of the liquid.
Pump producing low flow rate or head
- Leakage through casing, gasket, or O-ring. Repair the pump as necessary.
- Worn out or broken impeller. Replace the impeller.
- Excess clearance between the casing and impeller. Adjust the clearance.
- Partially clogged impeller. Remove the blocking material.
The pump stops after being started
- The pump is not well primed. Re-prime the pump.
- Vapour pockets or air on the suction line. Re-arrange the pipe to remove air pockets.
- Leakage through the suction line. Repair the suction line.
The pump produces a lot of noise or vibrations
- The motor and pump are not well aligned. Align the motor and pump shaft properly.
- Clogged impeller. Open the pump according to the guidelines given by the oil transfer vortex impeller pump manufacturer and remove materials clogging the impeller.
- Worn out bearings. Replace the bearings.
- Discharge/suction pipe not supported firmly. Tighten the suction/discharge pipe firmly.
Summary
An oil transfer vortex impeller pump is used in the transportation of oil and fuel and related products. This pump uses a vortex type of impeller. The impeller is meant to create a vacuum in the pump to force fluid to move from the tank into the pump. When the fluid gets into the pump, its kinetic energy is increased by the impeller rotating at a very high speed. The fluid then proceeds to the pump casing which reduces its velocity while increasing pressure energy on the liquid. This pressure energy ensures the fluid is capable of moving to the required destination.
Oil transfer vortex impeller pump manufacturers design various types of pumps among them single-stage pumps, multistage pumps, self-priming pumps, and magnetic drive pumps among others. Applications of this pump include heavy crude oil, lubricating oil, drilling mud, diesel, gasoline, kerosene, multiphase fluid transfer, polymer flooding, waste, and skimming applications among others. The advantages of this pump are simple and compact design, versatility, durability, easy installation and repair, high strength, corrosion resistance, and high reliability.