Submersible Axial Mixed Flow Pump
What is a submersible axial mixed flow pump?
A submersible axial mixed flow pump is designed to produce axial or mixed flow and to run in the pumped liquid. Submersible axial mixed flow pumps utilize a mixed flow impeller to discharge fluid in a conical direction using a combined radial and axial pumping action. A mixed flow falls between the axial flow (parallel to the shaft axis) and the radial flow (perpendicular to the shaft axis). Therefore, a submersible axial mixed flow pump combines the characteristics of axial and radial pumps and transports fluid in a semi-axial direction. Submersible axial mixed flow pump manufacturers develop the units to provide unique performance characteristics, such as a high pump capacity of up to 5500 gallons per minute, a discharge head of 50 feet, and a wide range of motor output. Submersible axial mixed flow pumps suit large flow rates and high discharge pressure applications. They are typically evident in industrial and municipal water, wastewater treatment facilities, irrigation firms, etc.

Figure: showing the configuration of a submersible axial mixed flow pump
Components of a submersible axial mixed flow pump
Electric motor
The electric motor provides power for running the submersible axial mixed flow pump. It is hermetically sealed and coupled to the pump head
Pump casing
The pump casing houses the pump’s internal components and guides the flow into the pump through the suction inlet and out of the pump through the delivery pipe.
Coupling
The coupling connects the motor to the pump head facilitating smooth transmission of rotary motion between the motor shaft and the pump shaft. The coupling design can be flexible, rigid, or close coupling. A flexible coupling can allow angular misalignment of up to 3 degrees and parallel misalignment to a certain degree. However, submersible axial mixed-flow pumps with flexible couplings are less common than those with rigid and close coupling.
Pump shaft
The pump shaft carries the impeller (s), mechanical seals, or packings. It is made of stainless steel and rides on bearings.
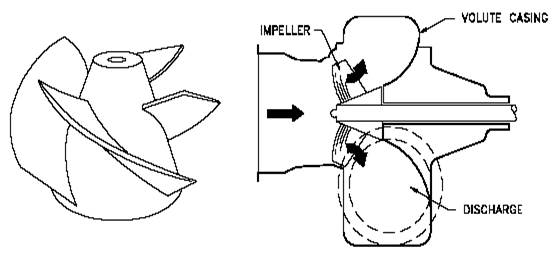
Mixed flow impeller
A submersible axial mixed flow pump uses a mixed flow impeller made from cast iron, cast steel, or stainless steel. The mixed flow impeller helps to move fluid semi-axially through the pump body. As the fluid flows through the pump, the impeller blades push the liquid away from the pump shaft and into the discharge port at an angle greater than 90 degrees.
Figure: showing a mixed flow impeller.
Self-cooling jacket
It provides high reliability and effectively dissipates heat.
Float-type leakage detector
It provides early warning of mechanical seal failure avoiding costly motor repairs.
How does a submersible axial mixed flow pump work?
The submersible axial mixed flow pump pushes water to the surface through a pipe connecting to one end of the pump. When the motor starts, the pump impeller rotates the water pre-filled in the pump casing, imparting high kinetic energy and velocity to the liquid. The impeller then throws the water semi-axially into the volute. In the volute, the fluid speed decreases due to the gradually enlarging flow path as the high fluid velocity converts into high static pressure. Finally, the water exits the pump under elevated pressure, which helps to push it to the surface and to direct the flow to the designated location via the delivery connections.
Types of submersible axial mixed flow pumps
Overhung submersible axial mixed flow pump
An overhung submersible axial mixed flow pump uses a single impeller installed on a shaft suspended at one end by bearings. In this pump, the impeller fits either vertically or horizontally. The motor of this pump can be flexibly-coupled, rigidly coupled, or close coupled to the pump body. Generally, the overhung submersible axial mixed flow pump has a more straightforward design due to single-bearing housing and single seal or packing.
Figure: Showing an overhung submersible axial mixed flow pump.
Between bearing submersible axial mixed flow pump
A between-bearing submersible axial mixed flow pump uses one or more impellers supported on a shaft that is suspended at both ends between two bearings. Using bearings at either end provides extra mechanical support to the rotor and enhances the ability to balance the axial load acting on the pump. The between-bearing design enables the pump to pump perfectly in applications requiring even higher flow rate and pressure and where there are possibilities of heavier loading.
Single-stage submersible axial mixed flow pump
A single-stage submersible relies on a single impeller to perform the pumping action. This pump is comparatively simple in design and low cost compared to the other submersible axial mixed flow pump. It is easy to install and has less volume.
Figure: Showing a single-stage submersible axial mixed flow pump.
Multistage submersible axial mixed flow pump
A multistage submersible axial mixed flow pump uses more than two impellers to perform a series of pumping stages. The impellers are mounted along the same shaft and housed in different chambers. The submersible axial mixed flow pump with multiple stages can manage significantly larger flow rates and higher-pressure heads than the single-stage counterpart.
Applications of a submersible axial mixed flow pump
Submersible axial mixed-flow pumps cater excellently to various applications worldwide, including industrial water, urban and rural municipal water, wastewater treatment, agricultural irrigation, amusement parks, effluent and process systems, and paper mills. They are used to do the following:
- Submersible axial mixed-flow pumps are widely used for pumping water from various sources, such as lakes, tanks, rivers, oceans, etc.
- They are also used to transport wastewater in water treatment plants.
- They are used to pump sewage and industrial water with suspended solids.
- They are used to pump water for recreation purposes in amusement parks.
- Submersible axial mixed-flow pumps supply water to agricultural firms’ sprinklers.
- They are used to solve flood resistance problems in rivers and lakes with large fluctuations in water level.
- They are used for low-lying dewatering regions and pumping seawater.
- They are used in large-scale drainage.
Advantages of a submersible axial mixed flow pump
- Due to the dual pumping action, submersible axial mixed-flow pumps provide large flow rates and high discharge pressure.
- They can pass large-diameter solids with high outputs, preventing clogging and lower operating costs.
- They can work with clear and contaminated or turbid liquids due to the unique design of the pump impeller.
- Submersible axial mixed flow pumps are self-priming since they run inside the pumped liquid.
- They are free of cavitation because there is no spike in pressure as the fluid moves through the pump.
- They have low life cycle cost due to minimal maintenance requirements. Also, the float-type leakage detector provides early warning of mechanical seal failure avoiding costly motor repairs.
- They are highly energy efficient and reliable in operation.
- They effectively dissipate heat to the surrounding liquid because the submersible axial mixed flow pump manufacturer fits the units with self-cooling jackets.
- They have a compact design that is easy to install and operate.
- They bring together the benefits of axial and radial flow pumps, providing high flow rates and discharge pressure.
- They are silent and free of vibrations.
Disadvantages of a submersible axial mixed flow pump
- The submersible axial mixed flow pump has a comparatively lower head.
- They are vulnerable to leaks and operation failures due to weary gaskets or corroded seals.
- It is not easy to observe the pump operation in the underwater environment and to detect the onset of failure.
- The submersible design is more technical and complex. Therefore, submersible axial mixed-flow pumps are more expensive than their surface counterparts.
- They may overheat if not fully submerged in the pumped liquid.
Troubleshooting a submersible axial mixed flow pump
The pump fails to start
- There are shortcomings in the motor wiring. Consult a licensed motor dealer to inspect the conditions of the pump wiring and repair any faults.
- The fuse is blown out, or the circuit breaker is tripped. Inspect the submersible axial mixed flow pump for a damaged fuse and replace it if necessary. Be sure to reset the circuited breaker if it is tripped.
- Dirty or corroded fuse receptacles. Inspect and clean fuse receptacles if necessary.
- The voltage is irregular due to dirt or corrosion at the pressure switch. Check the pressure switch and remove any debris.
The pump gives little or no discharge
- The pump is operating in reverse. Match the motor rotation with the direction indicated by the submersible axial mixed flow pump manufacturer on the pump casing.
- The check valve is faulty or wrongly installed. Inspect the check valve, install it correctly or replace it if necessary.
- There is an insufficient monomeric head. It occurs due to high friction losses exceeding the submersible axial mixed flow pump design. Increase the pump power to the required level. Be sure to open all the valves. Check that the delivery pipes are of the correct sizes according to the submersible axial mixed flow pump manufacturers’ guide.
- The pump inlet is blocked. Clear any obstruction from the pump inlet.
- The impeller, filter, or check valves are clogged. Inspect the components and clean any clogging material.
The motor overheats
- The motor is at the onset of failure. Consult a qualified submersible axial mixed flow pump dealer to inspect the motor condition or replace the motor if necessary.
- There is a voltage spike due to a storm or lightning strike. Fit the pump with an external surge protector.
- The pump is not fully submerged in operation. Check and fully immerse the pump if necessary.
- The thermostat is set too high. Ensure that the thermostat is set to the temperature level specified by the manufacturers of the submersible axial mixed flow pump.
- There is a heavy build-up of organic or mineral material outside the motor. Inspect and clean any build-up from the pump.
Thermal trip
- The driver overload. Ensure the pump is drawing the correct amount of current.
- The pump head is too low. Adjust the pump head or install a control valve to detect back pressure according to the set value.
- The stop level is too low. Verify the stop switch level from the submersible axial mixed flow pump manufacturer’s manual and adjust accordingly.
Low pump capacity
- There is excessive clearance between the impeller and the pump casing, causing the fluid to recirculate. Ensure that the pump impeller matches the size specified by the submersible axial mixed flow pump manufacturers.
- The suction is clogged. Clear the suction from any debris.
- The discharge pipe is blocked. Inspect and clear any blockage from the discharge pipe.
- The impeller is severely worn out. Inspect the impeller for wear and replace it if necessary.
The leakage detector is activated
- The detector cable is compromised by wear, damage, or contact with oils. Inspect the detector cable for faults and correct or replace it if need be.
Summary
A submersible axial mixed flow pump is a device meant to produce an axial or mixed flow of a pumped liquid while running inside the same liquid. Submersible axial mixed-flow pump manufacturers fit the device with a mixed-flow impeller to generate a combined axial and radial pumping action. A mixed flow lies between the axial flow (parallel to the shaft axis) and the radial flow (perpendicular to the shaft axis). As such, a submersible axial mixed flow pump combines the characteristics of axial and radial flow pumps. Submersible axial mixed flow pumps are perfect for large flow rates and high discharge pressure applications. They can be found in industrial and municipal water systems, wastewater treatment plants, amusement parks, etc. The unique design of the pump impeller allows the device to handle clear and contaminated liquids. Typical uses of a submersible axial mixed flow pump include pumping clean water, sewage, and industrial water with suspended solids. They are self-priming, non-clogging, cavitation free, highly efficient, and reliable.