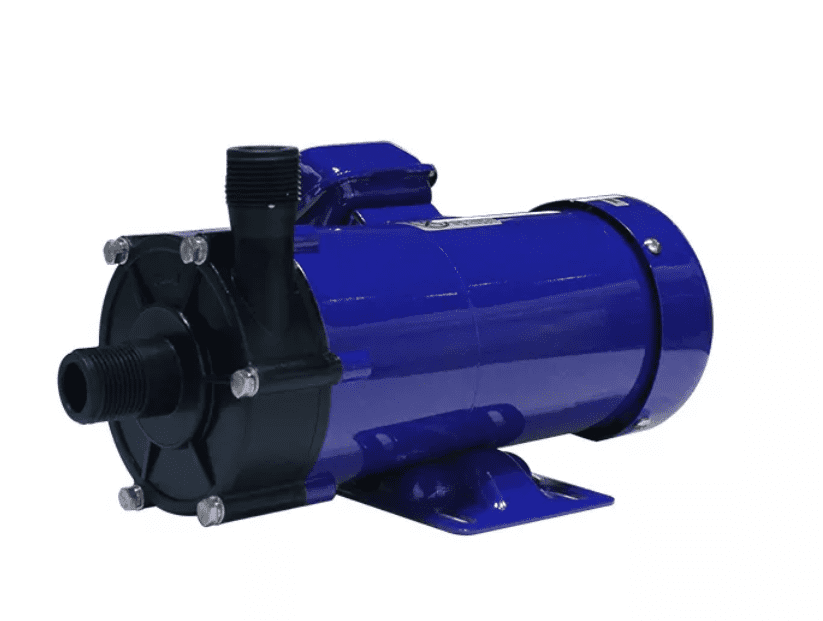
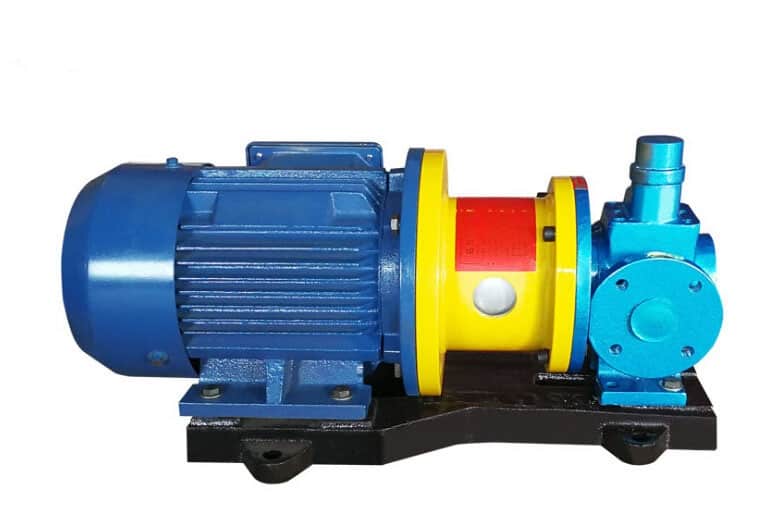
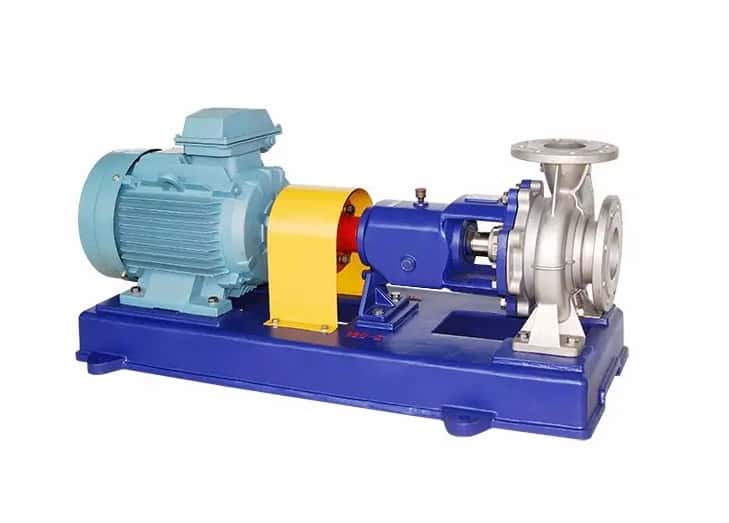
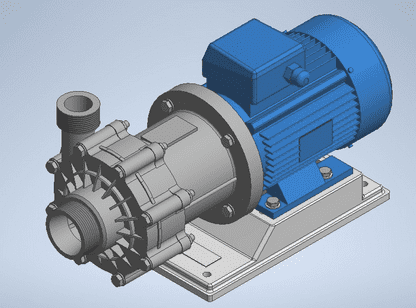
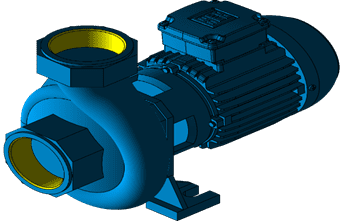
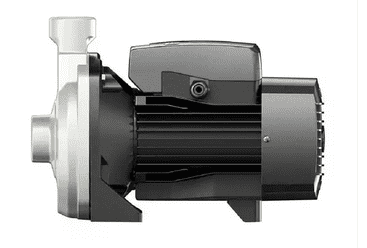
Magnetic Pump
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
What is the magnetic pump?
This is a seal-less pump that employs magnets to drive pump impeller to create pressure energy needed to transport the liquid. There are two magnets in this pump. The two magnets are arranged opposite to each other creating a magnetic field pattern. This pattern forces the drive magnet to rotate the driven magnet when the motor shaft rotates. This type of pump is very good in transporting hazardous and corrosive fluids which when leaked could lead to legal action or cause a high level of damage like fire. As such, magnetic pump manufacturers are constrained to follow strict regulations when designing this pump to ensure it will be free from any leakage when transporting hazardous fluids. The pump works by rotating its impeller to create a pressure difference between the inside of the pump and the sump. This pressure difference forces fluid into the pump. The pump then transports the fluid using pressure energy to the indented location.
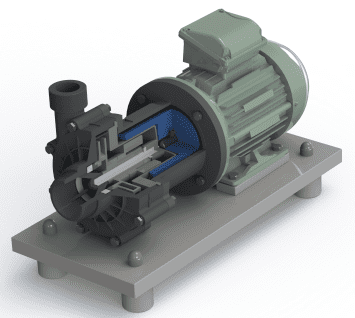
Fig: Magnetic pump
Components of a magnetic pump
Motor
The motor is the component responsible for providing the power that runs the pump. The motor is powered by electricity and it converts this electricity into mechanical power in terms of torque and speed.
Impeller
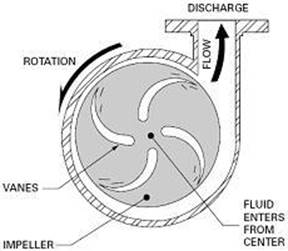
This is the component used to create a vacuum in the pump by rotating at a very high speed. This rotary motion is also used to impart kinetic energy to the fluid sucked by the pump making it move faster. The rotation of the impeller is supported by shaft sleeves and shaft bearings.
Magnets
The magnetic pump manufacturers design this pump with two magnets outer and inner magnet. The outer magnet ring faces inwards and it is mounted on the coupling housing. The inner magnet is mounted inside the pump. This arrangement is meant to create a magnetic field pattern to force the magnets to rotate each other when the motor shaft rotates.
Casing
This is a component that consists of the discharge and suction flanges and the volute that houses the impeller and bearings.
Containment shell
This is the last component of the fluid contact assembly. A gasket is used to seal this shell against the casing. Magnetic pump manufacturers make the containment shell from a non-metallic, high-strength, corrosion-resistant material.
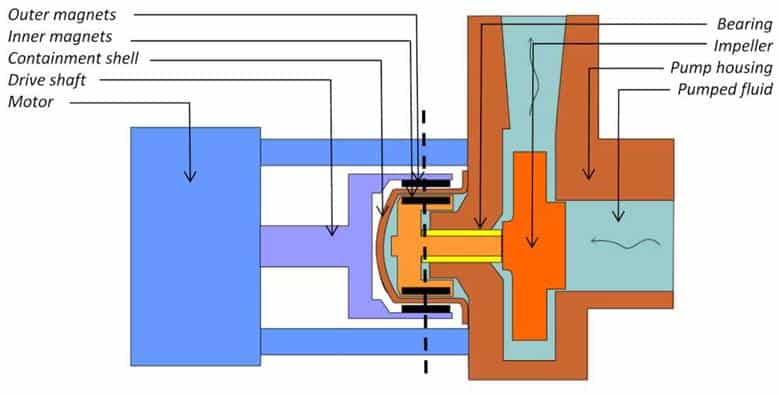
Fig: Components of a magnetic pump
How does a magnetic pump work?
A magnetic pump operates by use of magnetic technology. This technology involves two magnetic rings. The magnets are arranged with their north and south poles opposite to help create a magnetic field pattern. To start the pump, the motor is switched on. This forces the motor shaft to rotate. The rotation of the motor shaft forces the outer magnet to spin at the same speed. Due to the magnetic field pattern, the rotation of the outer magnet causes the inner magnet to rotate. The inner magnet then causes the pump impeller to rotate about the pump shaft.
Due to impeller rotation, a vacuum is created inside the pump. This vacuum causes the atmospheric pressure on the surface of the fluid source to force fluid into the pump. The fluid enters the pump through the suction pipe and it gets kinetic energy imparted on it by the impeller rotating at high speed. The liquid then proceeds to the casing where its kinetic energy is reduced and simultaneously pressure energy increased. This pressure energy is responsible for transporting the liquid to the required location.
Types of magnetic pumps
Stainless steel magnetic pumps
This is a magnetic pump that is made from stainless steel material. This material has good mechanical and thermal properties that make the pump work at high pressure and high temperatures. However, use of this pump is limited at certain temperatures since high levels of heat can damage the magnets and thus the whole pump. As such, the pump should be used at the temperatures recommended by the magnetic pump manufacturer. This pump has the advantage of being resistant to corrosion making it suitable for use in corrosive fluids like acids and alkalis. However, this pump is heavy due to the steel material used.
Figure: Stainless steel magnetic pump.
Plastic-lined magnetic pump
This is a magnetic pump whose interior is coated with a plastic material such as Teflon. Plastic materials are excellent in resisting corrosion relative to metallic ones. As such, this pump becomes the preferred choice for handling corrosive liquids like acids. The challenge associated with this pump is that it cannot be used at high temperatures since plastic would melt. As such, if the application would involve high temperature, then a stainless steel pump is recommended. Magnetic pump manufacturers design this pump for vertical or horizontal installation depending on the available space.
Figure: Plastic-lined magnetic pump.
Self-priming magnetic pumps
This is a magnetic pump that is designed to be automatically self-priming. This pump has close tolerance working components that trap liquid in the pump’s body to prevent it from returning from the discharge end to the suction side when the pump is not working. Magnetic pump manufacturers design this pump such that presence of liquid in the pump body can allow the pump to handle air pockets better. Air pockets refers to air bubbles accumulating in the working mechanism of the pump. Such bubbles do impair pump operation.
The pump works by rotating the impeller to draw air into the pump from the suction line. While drawing, it creates a liquid ring inside the pump casing. This leads to formation of a tight gas seal which stops air from returning from the exit side to the suction line. Bubbles of air are trapped in the liquid on the impeller vanes. The bubbles are then transported to the discharge side. The air is then expelled and only the liquid returns to the pump housing reservoir under gravity. The liquid rises the suction line as it is pumped. The process goes on until all the air in the suction pipe and the pump is replaced and then the normal pumping process starts and the liquid is discharged. When the pump is stopped, the priming chamber retains enough liquid that ensures the pump can prime when it is started again.
Figure: Self-priming magnetic pump.
Multistage magnetic pump
This is the type of pump in which the fluid flows through more than two impellers. Each pump stage is made up of an impeller and diffuser located in one casing. The impellers of this pump are not necessarily arranged in tandem. Balance of the axial thrust is enhanced by arranging the impellers back to back in groups or pairs. This pump is such that by having more stages or impellers, it produces more pressure energy. However, having a high number of stages will increase natural or external vibrations on the pump as well as cost.
Figure: Multistage magnetic pump.
Single-stage magnetic pump
This is a magnetic pump designed with one impeller. Most of these pumps are of small size relative to the multistage pumps. It is of simple structure, high speed, stable performance, lightweight, large flow, and high efficiency. This pump is cheaper relative to the multistage type. Magnetic pump manufacturers design this pump for vertical or horizontal installation.
Figure: Single-stage magnetic pump.
Applications of magnetic pump
- These pumps are used in pressure-boosting applications.
- Magnetic pumps are used in batch chemical processes.
- They are used in tanker unloading.
- These pumps are used in water treatment.
- It is used to transport water and water vapors in heat exchangers.
- They are used to transport corrosive liquids such as sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid.
- They are used to transport flammable products such as petroleum.
- Magnetic pumps are used in food and beverage processing plants.
- They are used to transport lubricants and cooling oils.
- They are used to transport cryogenic fluids.
Advantages of magnetic pumps
- Magnetic pumps are durable. Unlike pumps that use mechanical seals that need to be replaced often, magnetic pumps can be used for a long duration without replacing the magnetic coupling.
- They are versatile. This type of pump can be used in different industrial applications for transporting different liquids ranging from foods, acids, and water.
- Low maintenance and repair costs. This pump rarely breaks down due to a lack of mechanical seals. The use of magnetic coupling makes the pump suitable for use for over 10 years without any major repair if the pump is used according to the instructions given by the magnetic pump manufacturer.
- Free from leakage. This pump uses magnetic coupling meant to eliminate fluid leakage since there are no mechanical seals that can fail with time.
- They have a reliable working mechanism that hardly fails while the pump is in use.
- The pump does not have problems with misalignment. Magnetic pump manufacturers design the pump with an air gap between the magnet and the pump which eliminates their physical contact and thus no thermal expansion or misalignment which can cause wear or failure on the pump.
- It reduces fines. This pump is designed by adhering to strict regulations meant to protect the environment and enhance high levels of safety which means that the user can hardly get fined for damage caused by the pump through leakage.
Disadvantages of magnetic pump
- Use of this pump is limited to high temperatures since the magnets can get damaged.
- Magnetic pumps are recommended for use in clean liquids since solids in the liquid do stick on the magnets weakening pump performance or causing damage.
- Using the pump at high torque applications can easily damage the magnetic coupling and thus the whole pump.
- This pump is quite expensive relative to other pumps.
Troubleshooting magnetic pump
Low liquid flow rate
- The pump is not primed. Prime the pump suction line.
- High discharge pipe resistance. Check the discharge pipe for clogged material and remove them if any. Also, try to modify the pipe by reducing fittings and bends and cleaning them.
- Leakage through the suction line. Check the gasket and flange connections on the suction pipe. Tighten the flange bolts to attain the torque recommended by the magnetic pump manufacturer. Replace the gasket if it is leaking.
- Reverse rotation or low rotating speed. Change the direction of motor rotation. Also, check and correct the frequency and voltage of the motor as recommended by the magnetic pump manufacturer.
The flow rate is too high
- High motor speed. Check the motor frequency and voltage and adjust them as recommended by the magnetic pump manufacturer.
- Low discharge pipe resistance. Control the output liquid using the outlet valve.
- Different fluid viscosity. If the pump is used to pump fluid with a viscosity different from the one recommended, the flow rate will be different. Ensure the pump is used for the liquid recommended by the magnetic pump manufacturer.
Pump is noisy
- Worn out bearings. Replace the bearings with original new ones.
- Foreign materials clogged the impeller. Open the pump and clean off the materials.
- Loose connection of the bolts and nuts. Tighten the bolts and nuts.
Summary
A magnetic pump uses magnets to run the impeller. There are two magnetic rings in the pump. One magnet is mounted on the outside and the other one is on the inside. The outer magnet is the driver and the inner magnet is the driven. The drive magnet rotates when the pump is turned on. Rotation of the drive magnet forces the inner magnet to spin at the same speed as the motor shaft causing the impeller to rotate. Rotation of the impeller creates a pressure difference that forces liquid into the pump and then it is transported to the required destination.
Magnetic pump manufacturers produce various types of pumps which include single-stage pumps, multistage pumps, stainless steel pumps, plastic-lined pumps, and self-priming pumps among others. Applications of this pump include oil refinery, petrochemicals, corrosive and hazardous liquids, water treatment, foods and beverages, and cryogenic fluids among others. The advantages of this pump are durability, versatility, leakage proof, reliability, low maintenance, reduced fines, and corrosion resistance.