Electric Gear Oil Pump
What is an electric gear oil pump?
An electric gear oil pump is a positive displacement (PD) rotary pump that uses an electric motor as the prime mover. Electric gear oil pump manufacturers develop the device with a set of interlocking gears which act as the rotating element. The electric gear oil pump moves oil by repeatedly enclosing a fixed volume using interlocking gears, transferring it mechanically using a cyclic pumping action. It is particularly suited for pumping oils and other high-viscosity fluids and is found in hydraulic power systems and commercial and household lighting equipment. Electric gear oil pumps differentiate themselves by gear arrangement and can be either external or internal gear oil pumps. The external gear oil pump can sustain higher pressure and flow rates than the internal gear counterpart. However, the internal oil gear pump provides better suction capabilities. Generally, these edge-cutting devices have many outstanding benefits, such as low power consumption, high efficiency, and a compact and simple structure with few moving parts.

Figure: Showing the configuration of an electric gear oil pump
Components of an electric gear oil pump
Electric motor
The electric gear oil pump manufacturers fit the unit with an electric motor to drive the rotating element—the electric motor works by converting the electrical energy supply into mechanical energy output. An electric motor can be either an alternating or Direct Current (DC). Most units employ a DC brushless motor.
Pump body
The pump body or housing protects the rotating element and other internal components, such as the shaft, bearings, and shaft sleeves. The electric gear oil pump manufacturers usually seal the pump housing to prevent leakage and retain pressure. Electric gear oil pump manufacturers design the pump body from various materials such as brass, cast steel, or ductile cast iron.
Shaft
The pump is a rotary mechanical component supported by the bearing and connected to the driver gear. It connects the rotating element to the electric motor directly or via coupling. It is usually made from stainless steel because it is strong and can overcome vibration during pump operation.
Gears
The electric gear oil pump comprises a set of interlocking gears. One driver gear and one driven gear form the rotating element. The purpose of the gears is to move the fluid through the pump body. Electric gear oil pump manufacturers create these components from bronze, alloy steels, heat-treated carbon steels, etc.
Bearings
The bearings support the rotor assembly and ensure it aligns perfectly with the pump body. They carry the fully rotary load of the shaft during operation and minimize friction between the rotating shaft and the stator for smooth operation.
Mechanical seals
The mechanical seals prevent fluid under pressure from leaking out of the pump. Mechanical seals prevent the pump from drawing in the air under vacuum conditions.
How does an electric gear oil pump work?
An electric gear oil pump uses the rotating action of gears to move the fluid through the pump. When the electric motor starts, the rotating element turns, developing a liquid seal with the pump casing and creating suction at the pump inlet. As the gears come out of the mesh on the inlet side of the pump, they make an expanded volume. Oil is drawn into the pump casing and enclosed within the cavities developed between the gear teeth. The trapped oil is transferred from the inlet to the discharge around the pump casing. The interlocking gear teeth on the discharge side of the pump reduce the volume and force the fluid out under pressure. As long as the gears rotate, they intermesh and repeatedly enclose a fixed volume of oil and transfer it mechanically in a cyclic pumping action.
Types of electric gear oil pumps
Electric external gear oil pump
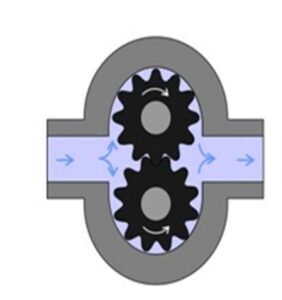
An electric external gear oil pump comprises two identical, interlocking gears riding on separate shafts. The driver gear, which is directly powered using an electric motor, drives the other gear (called the drive or idler gear). However, in some cases, both shafts may be driven by motors. Electric external gear oil pump manufacturers can fit the device with a spur, helical, or herringbone gears. Bearings on each side of the casing support the shafts. This type of electric gear oil pump features close tolerances between the gears and the pump housing, allowing the pump to develop suction at the inlet and protecting the fluid against leaking back from the discharge side. An electric external gear pump can sustain higher pressure and flow rates due to the use of a more rigid shaft and closer tolerances. It is mainly used in hydraulic power applications, typically in vehicles, lifting machinery, and mobile plant equipment.
Figure: Showing gear arrangement in an electric external gear oil pump.
Electric internal gear oil pump
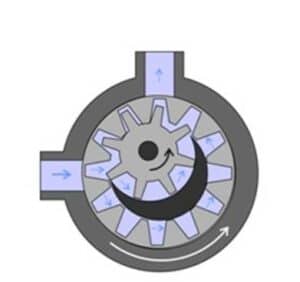
An electric internal gear oil pump comprises two interlocking gears of different sizes, one rotating inside the other. The larger gear, called the rotor, is an internal gear, meaning its teeth project on the inside. The smaller gear, called the idler, is located within the larger one and held in place using a pinion and a bushing attached to the pump casing. The idler gear is designed to interlock with the rotor such that the gear teeth engage at one point. An electric intern gear oil pump is perfect for shear-sensitive liquids such as soap and paints because it has better clearance and can operate at low speed. The electric internal gear oil pumps provide better suction capabilities and suit high-viscosity fluids. It also has a wide operating range and is easy to strip down, clean, and assemble.
Figure: Showing gear arrangement in the electric internal gear oil pump.
Applications of the electric gear oil pump
An electric gear oil pump perfectly fits various hydraulic power applications in vehicles, lifting machinery, and mobile plant equipment. They are also found in commercial equipment and household lighting equipment. Typical uses of electric gear oil pumps include the following:
- Electric gear oil pumps are used to lubricate the automatic or continuously variable transmission, particularly when starting or stopping the vehicle.
- They are used to pump high viscosity such as oil, paints, and resins.
- They are used for the transfer of low-viscosity oil, antifreeze (A), diesel (D), and water (W).
- Electric gear oil pumps are also widely used in applications requiring accurate dosing or high-pressure output.
- They are used in various applications with irregular supply because the pump output is only slightly affected by the pressure.
- They are used for metering and blending operations in chemical and agricultural applications because the pump output is directly proportional to the pump speed.
Advantages of an electric gear oil pump
- Electric gear oil pumps deliver a smooth, pulse-free flow proportional to the rotational speed of its gears.
- They provide higher pressure and throughputs than the vane or lobe pumps
- They are self-priming and can dry-lift, although their priming characteristics improve if the gears are wetted.
- They can be engineered to handle corrosive and viscous material by carefully selecting pump materials. Using composite materials can allow the pump to take corrosive liquids such as sulphuric acid, sodium hypochlorite, ferric chloride, and sodium hydroxide.
- Electric gear oil pumps are lightweight, compact, and straightforward due to few moving parts.
- They have high efficiency and low power consumption.
- They offer superior pressure and temperature characteristics.
- Electric gear oil pumps are less sensitive to cavitation.
- They are easy to operate, maintain and reconstruct.
- They are available in tiny sizes to supply constant liquid flow and pulseless discharge.
- The pump output is controllable.
Disadvantages of the electric gear oil pump
- An electric gear oil pump requires regular lubrication of the gears by the pumped fluid; thus, it cannot run dry for prolonged periods.
- The interlocking gears can be loud.
- Electric gear pumps are susceptible to wear, mainly when used with abrasive liquids, because of the close tolerance between the gears and the pump casing. To successfully handle oil with abrasive particles, a higher-capacity pump operating at low speed would be required to minimize pump wear. However, such a pump would operate at low volumetric efficiency.
- The volumetric efficiency of an electric gear oil pump is reduced at lower speeds and flow rates.
- They pump against back pressure, and any blockage downstream can cause pipework failure or the equipment.
Troubleshooting an electric gear oil pump
The motor fails to start
- The power cable is broken. Consult a licensed electrical technician to inspect and replace any broken wires.
- There is no power supply to the Control Panel, or the power supply is inadequate. Check the main input panel and ensure the power cable connections follows the electric gear oil pump guidelines.
- The fuse is blown-out, or the circuit breaker is tripping. Inspect the pump for a blown-out fuse and replace it if necessary. Be sure to reset the circuit breaker if necessary.
The motor is operating, but there is no fluid delivery
- The direction of motor rotation is wrong. Check the direction of rotation is in line with the arrow on the casing and nameplate.
- There is an air pocket in the suction line. Fill the suction line with fluid, slope the pipework upwards, and ensure there are no kinks in the suction line and that the pipework is as straight as possible.
- The relief valve has failed. Ensure the pressure setting is correct according to the electric gear oil pump manufacturer. Clean the relief valve.
- There is air ingress through the seal. Inspect the seals, pipework, and connected gaskets and correct them. Replace the pump seal if necessary. Inspect the pump O-Rings and replace them if necessary.
The pump ingresses too much air
- The pump speed is low. Increase the pump speed to the level recommended by the electric gear oil pump manufacturer.
- Pipe work connections are severely worn-out. Inspect, repair, or replace the pipe connections.
- The suction port sealing is defective. Inspect and repair pump sealing.
The pump cannot self-prime
- The motor direction is wrong/reversed. Inspect the motor rotation direction and switch the polarities if it is necessary. Ensure motor rotation matches the direction of the arrow provided on the nameplate by the electric gear oil pump manufacturer.
The pump is noisy
- The pump is cavitating. Use pipes of the correct diameter following the electric gear oil pump manufacturer. Reduce the suction head and clean filters. Also, try reducing the pump speed and raising the fluid level in the tank.
- Vibrations in safety valves. Adjust the pressure setting to the level recommended by the electric gear pump manufacturer or replace the safety valve if necessary.
- Gears are damaged. Inspect the gear and replace them if necessary.
- There is a significant pump misalignment. Inspect the pump and realign the components if necessary.
Summary
An electric gear oil pump is a type of positive displacement (PD) rotary pump that relies on an electric motor and inbuilt gears to move oil through the pump and pipe network. The electric gear oil pump manufacturers fit the units with two gears that interlock, constituting a rotating element to drive the liquid within the pump. The electric gear oil pump moves oil from one location to another by repeatedly enclosing a fixed volume using interlocking gears, transferring it mechanically through a cyclic pumping action. They are particularly suited for pumping oil and other high-viscosity fluids such as soaps, paints, and resins. Electric gear pumps are available in external or internal gear configurations. An electric external gear oil pump can sustain higher pressures (up to 7500 psi). In contrast, an electrical internal gear oil pump has better suction capabilities and is more suitable for high-viscosity and shear-sensitive fluids. Electric gear oil pumps provide numerous benefits, such as high efficiency, lower power consumption, and simple and compact design, which is easy to install and operate.