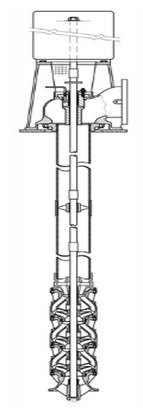
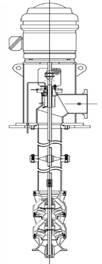
Vertical Turbine Pump
What is a vertical turbine pump?
A vertical turbine pump is a rotor dynamic pump consisting of modified radial flow impellers in a vertical orientation. It is meant for pumping water from underground borewells and deep reservoirs. The pump connects to a ground-level motor through a length vertical axis, hence the term vertical turbine pump. The vertical turbine pump manufacturers usually develop the unit in a multistage configuration comprising several levels of impellers enclosed in a bowl assembly. Each additional impeller increases the amount of pressure head the pump can generate while the flow remains constant. The vertical turbine pump manufacturers can design the pump for as much pressure head using as many stages as the bowl assembly can accommodate. Vertical turbine pumps can be installed in a suction barrel or below ground level to provide additional suction pressure head to the first stage impeller. In general, vertical turbine pumps are split into two broad categories: deep-well vertical turbine pumps and short-set vertical turbine pumps.

Figure: Vertical turbine pump
Components of a vertical turbine pump
Motor
The motor provides the mechanical power for running the pump. It can be either AC or DC motor and may contain either fixed or variable-speed drives.
Bowl assembly
The vertical turbine pump’s bowl assembly comprises the suction case, the impellers, and diffusing style casing. Each diffuser contains one impeller, and together they constitute a pump stage.
Figure: Configuration of a bowl assembly.
Pump casing
The vertical turbine pump employs a diffusing type of casing. The pump casing is a thin air- passage surrounding the impeller. It serves as a pressure containment vessel and directs the flow and out of the pump. The vertical turbine pump manufacturers create the pump casing using cast iron, carbon steel, or stainless steel to enhance strength, corrosion durability, and abrasion resistance.
Impeller
The impeller is a rapidly rotating fan consisting of blades that help move fluid from the pump’s inlet to the outlet by increasing the kinetic energy and pressure. In a vertical turbine pump, the impeller is positively locked to the pump shaft using precision machined taper locks. The impeller can be open, semi-open, or closed impeller type. Vertical turbine pump manufacturers develop the impeller with a wide range of hydraulic coverage for maximum efficiency.
Shaft
The vertical turbine pump’s shaft is a long cylindrical piece of metal centrally located in the pump and supported on bearings. It carries the impellers and connects the motor to the pump head through a flexible coupling. The pump shaft is usually designed for maximum strength and excellent corrosion resistance using high-end materials such as stainless steel, alloy steel, carbon steel, etc. It is also grounded and polished to provide a smooth bearing surface.
Coupling
The vertical turbine pumps use a flexible coupling, allowing for easier servicing of thrust bearings and mechanical seals. The coupling connects the pump shaft to the motor shaft facilitating the transfer of torque and rotation of the impellers. The coupling is precision machined and balanced for perfect alignment and power transmission.
Suction inlet
A vertical turbine pump’s suction outlet features a hydrodynamic design which helps to ensure smooth entrance flow. It also contains an oversized inlet strainer that prevents solids from entering the hydraulic assembly. The water enters the pumps through the suction Inlet.
Discharge outlet
The water exits the pump through the discharge outlet. The vertical turbine pump’s discharge outlet features a fabricated or fully cast heavy-duty and low-loss design.
How does a vertical turbine pump work?
A vertical turbine pump works by converting the mechanical of an impeller into kinetic and pressure energy of the pumped liquid. When the motor starts, the impeller rotates, creating a vacuum inside the pump casing. As a result, the water enters the first chamber due to the atmospheric pressure acting on the water’s surface. Once the water hits the first stage impeller, the mechanical action imparts high kinetic energy to the liquid. The impeller then throws the water into the volute, where the fluid’s pressure increases due to a reduction in its speed, and the water enters into the second stage, where fluid pressure further increases. This process continues until the last pump stage, where the fluid attains the required pressure head and pumps to the desired location via the discharge outlet and delivery pipe.
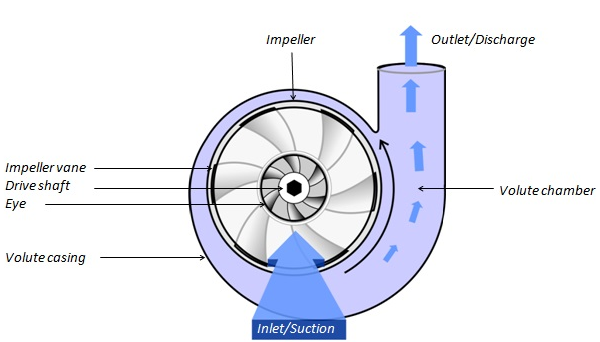
Figure: Working of a vertical turbine pump
Types of vertical turbine pumps
Deep-well vertical turbine pump
A deep-well vertical turbine pump is usually installed in a drilled well, with the first stage sitting below the water level. Vertical turbine pump manufacturers create the devices with a multistage assembly, self-priming ability, and mainly for water transportation. The deep-well vertical turbine pump is mainly used in transporting water from the deep well to storage tanks or treatment facilities on the surface.
Figure: showing a deep-well vertical turbine pump.
Short-set vertical turbine pump
Short-set vertical turbine pumps are typically shorter than 50 inches. They are common in all industries and water-handling applications but are primarily found in water pits. In relatively clean water applications, this pump’s bearing can lubricate using the pumped water. In contrast, an external water source, grease, or oil is used in applications where the pumped liquid cannot lubricate the bearings.
Figure: showing a short-set vertical turbine pump.
Stainless steel vertical turbine pump
A stainless-steel vertical turbine pump features a fully stainless-steel pump construction and can either be semi-submerged or fully immersible in water. It excellently operates in harsh environments where conventional vertical turbine pumps made from cast iron or steel cannot. This pump can be used as a deep well pump, wet pit pump, or submersible pressure booster pump. They are widely preferred for their versatility and durability.
Figure: showing a stainless-steel vertical turbine pump.
Double-stage vertical turbine pump
A double-stage vertical turbine pump comprises two impellers housed in separate diffusing pump chambers but mounted onto a single bowl shaft that passes through the middle of the diffusers. This pump provides the functionality of two pumps linked in a series.
Figure: showing a double-stage vertical turbine pump.
Multistage vertical turbine pump
A multistage vertical turbine pump consists of more than two impellers housed in different pump chambers mounted in series. Water enters the first chamber at suction pressure and exits from the last chamber at elevated pressure. This pump can manage higher pump head and flow rates than the double-stage counterpart and can work with a smaller motor.
Applications of a vertical turbine pump
Vertical turbine pump manufacturers develop the pump to serve excellently in applications with a low net positive suction head (NPSH). They are found in power plants, irrigation schemes, and water treatment plants.
- They are used hydraulic turbines to generate power because they can run in reverse. When the vertical turbine pump is employed for this application, the suction nozzle acts as the turbine’s outlet, while the discharge nozzle acts as the turbine’s inlet. This alteration has no impact on the device’s efficiency; the device’s efficiency as a turbine equals the efficiency when used as a pump.
- They are used as booster pumps in municipal pumping systems.
- They are used for providing flow for the cooling tower in power plants.
- There are used for transporting water in treatment plants.
- They are used for pumping raw water to irrigation sprinklers in irrigation farms.
- They are used for transporting water to faucets in homes.
- They are used to supply groundwater to municipalities that cannot rely on surface water.
- They also provide plant make-up water and fire water for industrial plants.
Advantages of a vertical turbine pump
- Vertical turbine pumps have high hydraulic efficiency.
- They have high energy efficiency due to the ability to work with smaller motors.
- They are perfect for high-head and low-flow applications.
- They have minimal leakage loss because the head per stage is less.
- They have compact construction with small impellers because the head per stage is less.
- They provide a stable performance.
- They have a low life cycle due to minimal maintenance requirements.
- They provide an easy and efficient way of pushing water from deep underground bore wells to the surface.
- They are highly versatile in applications, catering to agricultural irrigation, municipal water supply, power generation plants, etc.
- They are self-priming because the first stage impeller lies below the water level.
- They are highly reliable.
Disadvantages of a vertical turbine pump
- They require a large amount of headroom for installation.
- It is not easy to balance hydraulic thrust on vertical turbine pumps because of their overhang shaft, particularly in applications with high suction and high pressure.
- They can handle fluid with entrained or dissolved gases because the gas accumulates in the sealed chamber, where venting is complicated.
- The initial acquisition and installation cost of the pump is relatively high.
Troubleshooting a vertical turbine pump
The pump won start
- There is a blown-out fuse or tripped circuit breaker. Inspect the vertical turbine pump for a blown-out fuse and replace it if necessary.
- The voltage is irregular due to dirt or corrosion at the pressure switch. Inspect the pressure switch and clean it of any debris or pollution.
- The fuse receptacles are dirty or corroded. Inspect and clean fuse receptacles if necessary.
- The power supply to the panel is insufficient. Ensure that the motor receives the right amount of voltage and current.
Not enough water is running through the pump system
- The pump is air bound. Ensure that the pump system is free of air.
- The check valve has failed or is wrongly installed. Inspect the check valve, install it correctly or replace it.
- Clogged impeller. Inspect the impeller and remove any material.
- The pump is operating in reverse. Check that the direction of the motor rotation matches the direction indicated by the vertical turbine pump manufacturers on the nameplate. Be sure to reverse the motor polarities.
There is excessive pump vibration
- There are unbalanced components in the vertical turbine pump. Inspect and rebalance the elements.
- The impellers are severely worn-out or defective. Inspect the impellers and replace any worn-out impeller with another one from the pump manufacturer if necessary.
- Oblique or unbalanced shaft. Inspect the pump’s shaft and rebalance it as needed.
- The pump assembly is loose. Tighten pump components to the torque level recommended by the vertical turbine manufacturers.
Motor is overheating
- The motor is defective. Inspect and replace the prime mover if it is necessary.
- The motor is poorly installed. Ensure the pump is installed to the vertical turbine pump manufacturer’s standards.
- The vertical turbine pump is working cavitation. Check that the pump works within the correct speed range and uses the right impeller type.
- Poor coupling alignment. Be sure to realign the pump and coupling. Also, check the coupling rubber for wear.
- The pump grease is excessive or contaminated. Drain the excess oil or bearings and housing.
- There is an airlock in the pump. Loosen the vent plug to purge air.
Summary
A vertical turbine pump is a rotor dynamic pump designed with multiple modified radial flow impellers in a vertical orientation. The vertical turbine pump features a multistage configuration with several levels of impellers enclosed in a bowl assembly. It is meant for pumping water from underground borewells and deep reservoirs to storage tanks on the surface. The pump connects to an underground-level motor through a length vertical axis, hence the name vertical turbine pump. Vertical turbine pump manufacturers develop the pump to work perfectly for low net positive suction head (NPSH) applications. Because the vertical turbine pump can generate high pressure while the flow remains unchanged, it is also perfect for high-head and low-flow applications. Vertical turbine pumps have no priming issues and are energy and hydraulic efficient. They are commonly used in power plants, irrigation schemes, and water treatment plants. However, it is not easy to balance vertical thrust on vertical turbine pumps, and they are also quite expensive to acquire.