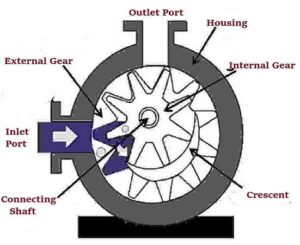
Magnetic Gear Pump
What is a magnetic gear pump?
This is a positive displacement pump that uses magnetic technology to connect the motor and the pump. The magnetic pump works by sealing off a certain amount of fluid using intermeshing gears. The liquid is moved when gears rotate. This type of pump transmits a pulseless fluid flow whose amount is proportional to the speed of the gears. This pump is suitable for use where high pressure is needed such as in adhesives, hydrocarbons, motor oils, and liquid fuels among others. This type of pump has a fixed displacement of fluid flow. This means that the pump can deliver a constant flow rate at a uniform speed despite pressure changes. Therefore, for every rotation of the gear shaft, there is a constant amount of fluid flow. Magnetic gear pump manufacturers design this pump with two gears that is driver gear and driven or idler gear. The drive gear is powered by the motor through magnets. The pump uses two magnets that are the drive and the driven magnet. The driven magnet rotates the pump driving shaft containing.
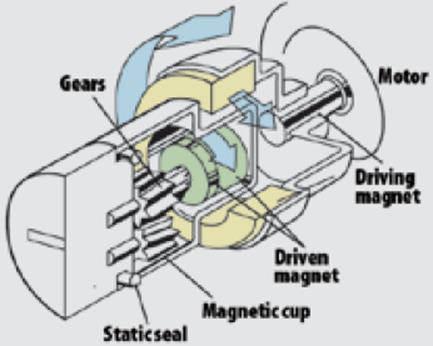
Figure: Magnetic gear pump
Components of a magnetic gear pump
Motor
The motor is the component that provides power to the pump. The motor works by converting electrical energy to mechanical energy that drives the pump.
Magnets
There are two magnets the drive (outer magnet) and the driven (inner magnet). The outer magnet is powered by the motor through the motor shaft. The outer magnet rotates the inner magnet through magnetic field force.
Driving gear
This is the gear that is powered by the motor through magnetic coupling. This gear rotates at the same speed as the motor.
Idler/driven gear
This is the gear that meshes with the driving gear. Due to the mesh, this gear is powered by the driving gear and thus it rotates in the opposite direction.
Housing
The housing is meant to cover the gears and other internal parts of the pump. Magnetic gear pump manufacturers make the housing using strong metallic materials to make sure the pump can withstand high pressure.
Inlet section
This is the part where the fluid gets into the pump. Liquid at low pressure enters the pump from this side.
Outlet section
This is the part that delivers the liquid to the required destination. This part is connected to the pipe that goes all the way to where the liquid is required.
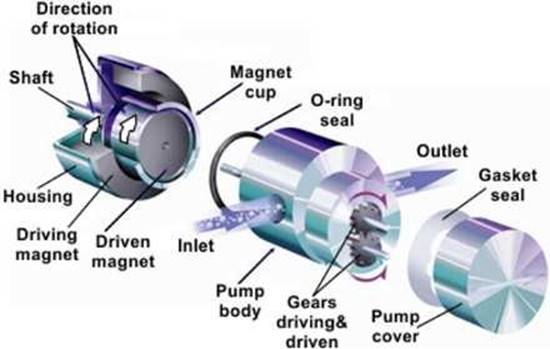
Figure: Components of a magnetic gear pump
How does a magnetic gear pump work?
This type of pump operates by using a rotating gear motion to transport liquid. This operation is based on the principle of a positive displacement pump. To start the pump, the motor is turned on. This allows electricity supply into the motor. As such, the motor shaft starts rotating at high speed. The shaft rotation forces the outer magnetic ring to rotate at the same speed. Due to the magnetic field pattern created between the outer and inner magnet, the inner magnet starts rotating at the same speed. The inner magnet is connected to the driving gear shaft so that they rotate at the same angular velocity. Rotation of the driving gear shaft leaves the driver gear in rotation.
Since the driver and driven gear are in mesh, the driven gear rotates in the opposite direction. Due to the rotation of the two gears, a partial vacuum is created on the pump inlet section. As such, the liquid on the suction side of the pump is sucked into the gears. Once the liquid is sucked, it is blocked between the housing and the gear. The blocked liquid between the housing and the gear teeth moves when the gear teeth rotate while the fluid flows from the inlet to the outlet side. The same applies to the driven gear where the fluid moves from the inlet side to the outlet side. The fluid is discharged through the outlet side of the pump. The driver and driven gears are fully in mesh with each other and thus there is no room for the liquid to move. As such, the liquid cannot flow directly to the discharge side or from the suction side to the outlet side. The liquid can only flow through the pump when there is rotation of the gears otherwise the liquid cannot flow.
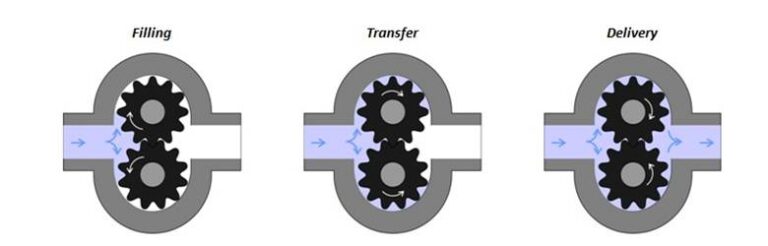
Figure: Working of a magnetic gear pump
Types of magnetic gear pumps
Magnetic external gear pump
This is a magnetic gear pump designed with identical gears. The two gears rotate in opposite directions. The driving gear is powered by the electric motor through the magnetic coupling so that it can drive the idler gear. Each gear is mounted on a shaft that is supported by bearings. When the gears on the inlet side come out of the mesh, the liquid volume increases on the suction side. When the gears start spinning against the pump casing, the liquid moves into the cavity and gets trapped by the gear teeth. The trapped fluid moves around the casing from the inlet to the outlet. When the gear teeth mesh on the outlet side of the pump, the volume of liquid reduces and the liquid is drained under pressure.
Magnetic gear pump manufacturers design the pump such that the liquid cannot return from the center between the gears if the gears are in mesh. Because of the tight tolerance between the pump gears and the housing, the pump produces suction on the inlet side and prevents fluid from returning from the outlet side. For this type of magnetic gear pump, spur gears, helical gears, or herringbone gears can be used.
Figure: Magnetic external gear pump.
Magnetic internal gear pump
This pump works similarly to the external type of gear pump but it has a dissimilar size of the two gears. One of the meshing gears rotates in the other gear. The internal gear is the larger one and its teeth protrude inwards. The smallest external gear within this area is located eccentrically. Magnetic gear pump manufacturers design this pump such that the gears mesh at specific points. The idler gear is held in place by use of a pinion and bushing mounted in the pump. This pump is non-pulsating and it can run dry for a short time. It is also bi-directional making it suitable for loading and unloading vessels. This magnetic gear pump is reliable and easy to maintain and use.
The volume of liquid increases when the gears on the inlet side are disengaged. As the gears rotate relative to the housing, the liquid moves into the pump cavity and it is trapped by gear teeth. The trapped liquid then moves around the housing from the suction to the discharge side. When the outlet side gears mesh, the liquid volume reduces, and the liquid is drained.
Figure: Magnetic internal gear pump.
Sanitary magnetic gear pump
This pump designed to enhance high levels of hygiene. Magnetic gear pump manufacturers design this pump for use in applications that need high levels of hygiene such as foods and beverage processing and pharmaceuticals. The hygiene levels in this pump are achieved by considering several factors such as the material used to make the pump and design considerations. The material used must be inert to the product being transported and also be safe for human consumption. The design should make the pump easy to clean to ensure there are no odors or accumulation of dirt inside the pump.
The efficiency of the magnetic gear pump
There are two main factors that affect the efficiency of a magnetic gear pump:
Gear clearance. When the gear clearance is large, it leads to fluid leakage. However, such clearance helps to reduce energy wastage by trapping fluid between the gear teeth.
Clearance. The clearance between the outside diameter and the end of the gear allows backflow and fluid leakage. However, increasing this clearance reduces hydrodynamic friction and thus it improves efficiency.
Applications of magnetic gear pump
- Magnetic gear pumps are used in the food industry in applications such as the transportation of vegetable oils, sugar, molasses, cacao butter, fillers, chocolate, and many others.
- This pump is used in paper and pulp industries to transport latex, sludge, lime, kaolin, lye, black liquor, acid, soap, and other products.
- It is used to transport resins and adhesives.
- The magnetic gear pump is used in chemical processing plants to transfer mixed chemicals, acids, isocyanates, plastics, and sodium silicate among others.
- It is used in paint and ink industries.
- It is used in petrochemicals such as crude oils, lube oils, pitch, diesel oils, bitumen, and similar products.
- They are used in water supply and water treatment.
Advantages of magnetic gear pumps
- Has long service life. This pump uses magnetic technology to couple the driving gear shaft to the motor. The magnetic coupling rarely breaks down thus enhancing the service life of the pump.
- Insensitive to fluid density and viscosity. Unlike the centrifugal pump which tends to be affected by fluid viscosity, this pump can move high and low viscous fluids by using its positive displacement characteristic.
- Magnetic gear pumps allow fluid flow by ensuring constant and even flow. Every rotation of the gear produces a specific volume of fluid despite the pressure.
- These pumps are self-priming, unlike centrifugal pumps.
- These pumps tolerate contamination, unlike other pumps that get clogged by dirt.
- The magnetic gear pump is bi-directional allowing its use for both loading and unloading.
- They are of compact and simple design.
- It has high efficiency when pumping highly viscous fluids since there is minimal or no leakage.
Disadvantages of magnetic gear pump
- These pumps use gears in mesh and thus use of abrasive fluids is a challenge.
- They make high levels of noise.
- Magnetic gear pumps are of small size and thus they cannot be used for high-capacity fluid flow rate.
Troubleshooting magnetic gear pump
The pump rotates but there is no liquid flowing
- The suction valve is closed. Open the suction valve.
- Low net positive suction head (NPSH). Increase NPSH.
- Air leakage into the pump. Repair the pump.
- The supply tank is empty. Fill the tank with the liquid to be pumped.
- Clogged strainer. Open the strainer and remove blocking materials.
- Closed discharge valve. Open the discharge valve.
Low fluid flow
- The pump running very fast. Reduce the pump speed.
- Leakage in the pump. Check the pump for any leakage and repair it as necessary.
- The suction valve is not fully open. Open the valve fully.
- Clogged strainer. Remove any blocking material on the strainer.
- The liquid temperature is too high. Operate the pump at the temperature recommended by the magnetic gear pump manufacturer.
The pump produces excess pressure
- The motor speed is too high. Reduce the motor speed by regulating the voltage and or frequency.
- High fluid viscosity. Ensure the liquid is as recommended by the magnetic pump manufacturer.
- The discharge valve is closed. Open the valve.
Summary
A magnetic gear pump uses magnetic technology to connect the pump and the electric motor. This magnetic technology uses two magnetic rings arranged with their poles opposite to each other. Such an arrangement is meant to create a magnetic field pattern. One of the magnets (outer magnet) is powered by the motor shaft when the motor rotates. Due to this rotation, the inner magnet rotates. This inner magnet has its shaft with the driving gear so that the gear can rotate when the motor is powered. The rotation of driving gear rotates the driven gear since the two are in constant mesh. The rotation of the two gears moves fluid from the inlet to the outlet side of the pump.
Magnetic gear pump manufacturers produce various types of pumps among them sanitary pumps, external gear pumps, and internal gear pumps among others. Applications of this pump include foods and beverages, paper and pulp, chemicals, and petrochemicals among others. The advantages of magnetic gear pumps are durability, ease of operation and maintenance, constant and even fluid flow, simple and compact design.