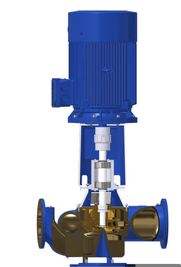
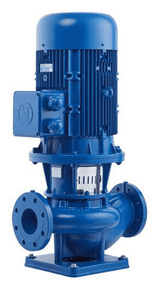
Vertical Inline Centrifugal Pump
What is a vertical inline centrifugal pump?
A vertical inline centrifugal pump consists of the suction and discharge ports oriented straight to the piping system, i.e., the centerline of the pump’s inlet and outlet is on the same level. It is specifically designed for vertical installation. The inline design provides a smooth flow of the pumped liquid through the system. Because of the vertical orientation, the vertical inline centrifugal pump is perfect for small pump rooms and other installations where space is confined. The vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturers develop the units for the electric drive only and to provide a wide range of flow rates and pressure heads. Vertical inline centrifugal pumps are ideal for transporting low-viscosity fluids such as water and some chemicals. They also apply as circulator pumps in applications where the water flowing through a pipe network needs to be pressurized. In most industrial uses, vertical inline centrifugal pumps suspend along the pipeline like valves.
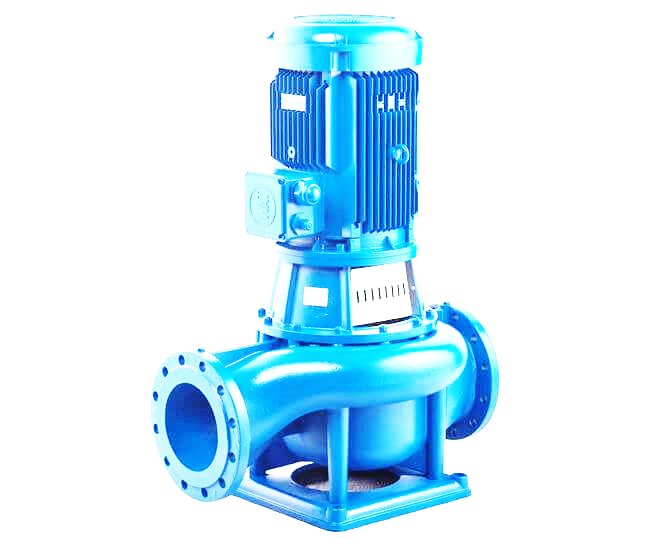

Figure: Vertical inline centrifugal pump
Components of vertical inline centrifugal pump
Motor
The motor acts as the pump’s prime mover, providing the mechanical power to run the pump. The vertical inline centrifugal pump uses an AC electric induction motor which in most cases is close-coupled to the pump body.
Pump casing
The pump casing houses the pump’s internal components and acts as a pressure containment vessel. It is usually made from cast steel or cast iron and sealed to prevent leakage. It contains a diffusing chamber that helps to convert fluid velocity to pressure head and guide the pumped liquid to the outlet.
Shaft
The shaft is a stainless-steel solid supporting the impeller and riding on the bearings.
Coupling
The purpose of the pump coupling is to connect the motor shaft to the pump head. The coupling can be either flexible or rigid. A flexible coupling accommodates minor shaft misalignment, while a rigid coupling does not. Monoblock vertical inline centrifugal pumps do not have any coupling because the impeller is directly attached to the motor shaft.
Impeller
The function of the impeller is to impart kinetic energy to the pumped liquid and move it through the pump body. Like the pup casing, the impeller is made from various materials such as cast steel, ductile cast iron, and alloy steel. The vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturers mainly use closed-type impellers with either single-suction or double-suction designs.
How does a vertical inline centrifugal pump work?
A vertical inline centrifugal pump operates on the principle of the forced vortex. This principle states that when a mass of fluid rotates due to an external force, its pressure head rises, leading to fluid transfer from one location to another. When the electric motor is started, the impeller rotates, creating a vacuum inside the pump casing. Water flows into the pump casing through the suction port to fill the void. Once the water strikes the impeller, the centrifugal force acting on the vanes rotates it radially and axially outwards until it passes through all of the impeller components and enters the diffuser at a very high speed. In the diffusing chamber, the water speed gradually decreases, leading to the high fluid velocity conversion into a high-pressure head. The diffuser then guides the water to the pump outlet and into the piping network to be transferred to the designated location.
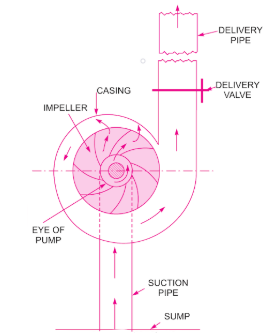
Figure: Working of a vertical inline centrifugal pump
Types of vertical inline centrifugal pumps
Monoblock vertical inline centrifugal pump
Monoblock vertical inline centrifugal pumps are suited for light duties and short operation periods at full motor speed. A monoblock vertical inline centrifugal pump consists of a single shaft connecting the motor to the pump head. The motor bearings carry the full rotary load of the shaft during pump operation. However, repairing the internal components is difficult because a standard shaft motor cannot apply, and sourcing must be from the original vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturers.
Figure: Monoblock vertical inline centrifugal pump
Rigidly coupled vertical inline centrifugal pump
A rigidly coupled vertical inline centrifugal pump has a separate motor & pump shaft which must be aligned and firmly fixed using a coupling. Each shaft has a short sleeve surrounded by a perpendicular flange. A coupling sits on each shaft so the two flanges line up face to face. A series of screws or bolts then hold the flanges together. The rigidly coupled vertical inline centrifugal pump is robust and easier to repair.
Vertical inline centrifugal pump with a spacer coupling
The motor shaft connects to the pump head via a flexible coupling in a vertical inline centrifugal pump with spacer coupling. A flexible coupling features a separate bearings assembly in addition to the motor, allowing for minor misalignment between the motor and pump shaft. The separate bearing assembly ensures that the radial loads are evenly distributed over many components. This type of vertical inline centrifugal pump is easy to maintain. Therefore, it is ideal for applications requiring short maintenance periods and low downtime, e.g., fire pumps and boiler feed pumps.
Figure: Vertical inline centrifugal pump with spacer coupling.
Single-suction vertical inline centrifugal pump
In a single-suction vertical centrifugal pump, the pumped liquid enters from one side of the pump impeller and exits from the other side. This pump is compact in construction and provides smooth operation.
Figure: Single-suction vertical inline centrifugal pump
Double-suction vertical inline centrifugal pump
The double-suction vertical inline centrifugal pump consists of a back-to-back impeller. The impeller design is such that the fluid enters the impeller from either side and discharges from the middle section. The double-suction vertical inline centrifugal pumps can manage higher flows than single-suction. The flow at the pump inlet is also comparatively low; thus, the pump can operate without cavitation.
Application of vertical inline centrifugal pumps
A vertical inline centrifugal pump caters to a wide scope of industrial, civil, and commercial applications. They are vital components in many industrial systems, including hydrants, deluge, monitor, and hot water systems. Typical uses of vertical inline centrifugal pumps include the following:
- Vertical inline centrifugal pumps are used for irrigation in agricultural farms.
- They are used to transport water for different uses in homes and industries.
- They are used in cleaning and industrial recirculation system.
- They also apply to move water in municipal works and water supply systems.
- They are also used as booster pumps in water supply systems.
- They are used for air conditioning in commercial buildings.
- They are used to supply and circulate water in hot water heating systems.
- They are used for firefighting and as boiler feed pumps.
Advantages of vertical inline centrifugal pump
- Vertical inline centrifugal pumps have high efficiency and can tolerate higher temperatures and pressure.
- Vertical inline centrifugal pumps are easier to install due to the compact design and simplified piping network.
- They are excellent for high-pressure and temperature applications.
- They have high reliability and are energy efficient.
- Vertical inline centrifugal pumps provide a space-saving design because the motor and service clearance lay above the pump casing; hence less floor space is required for pump installation.
- Vertical inline centrifugal pumps have higher Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) than suction pumps.
- The monoblock design eliminates coupling and shaft alignment, hence easier pump servicing.
- Vertical inline centrifugal pumps have low noise and vibration because the vertical shaft is naturally balanced, and the gravitation force does not act against the direction of shaft rotation.
Disadvantages of vertical inline centrifugal pump
- Vertical inline centrifugal pumps require vertical clearance for installation and maintenance.
- The weight of the pump accumulates below the volute, which can lead to stress concentration.
- They are challenging to maintain because the maintenance technician must disconnect the motor and the impeller from the volute to service the mechanical seals. This is mainly a significant challenge with large prime movers exceeding 25 hp.
- Vertical inline centrifugal pumps may experience mechanical seal problems.
- The mechanical seals may dry out or fail due to infiltration and accumulation of gases in the seal chamber. Leakage in the mechanical seals can damage the motor.
- They are vulnerable to corrosion due to seal leakage above the pump casing.
Vertical Inline centrifugal pump troubleshooting
Zero discharge after startup
- The pump inlet is blocked. Clear the channel of any obstruction.
- The inline pump operation is reversed. Check that the direction of the motor rotation matches the direction of the vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturer’s arrow indicated on the pump casing. Reverse the motor polarities.
- The monomeric head is insufficient due to high friction losses exceeding the pump design. Increase pump power to the level recommended by the vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturers. Open all the valves and make sure the delivery pipes are of the correct sizes
- There is air in the pump or suction pipework. Vertical inline centrifugal pumps cannot prime with air on the suction side. Ensure that the pump or pipework is filled with water to drive out the air from the pump system.
- The impeller or check valves are clogged. Clear any blockage from the impeller and the valves.
The pump is vibrating excessively
- The impeller is severely worn out. Inspect and replace the impeller with another one from the vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturer if you find it fit.
- There are unbalanced components in the pump. Inspect and rebalance the vertical inline centrifugal pump components as necessary.
- The pump shaft is oblique or unbalanced. Inspect the post, rebalance it as required, or replace it.
The noise level is too high
- Some pump components are excessively worn-out. Inspect the rotor assembly for worn-out bearings or impellers and replace them if necessary.
- The pump is working in cavitation. Ensure that the net suction pressure head meets the vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturer’s specifications. Be sure to open the suction line valves fully.
- The pump is working outside the duty range. Ensure the correct duty range according to the vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturer’s manual.
- Some parts are loosely tightened. Tighten the pump components to the torque level recommended by the vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturers.
Bearing overheating
- The coupling alignment is poor. Inspect and align the coupling correctly.
- The lubricating oil is insufficient or contaminated with dirt. Ensure the oil level matches the vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturer’s specifications. Use clean lubricating oil.
- There is excessive grease in the bearing housing. Drain the excess grease. Maintain the oil at the level recommended by the vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturers.
The pump driver is overloaded
- The pump’s speed is too high. Lower the pump speed.
- There is mechanical friction within the pump. Inspect the pump assembly for any obstruction or deflection.
- The density and viscosity of the liquid exceed the pump design. Ensure that the vertical inline centrifugal pump suits the particular application.
- Wrong voltage supply. Check that the pump receives the right amount of voltage following the vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturer.
Summary
The vertical inline centrifugal pump has suction and discharge nozzles lying in a straight line of piping. Vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturers specifically develop the units for vertical installation. The vertical orientation of the vertical inline centrifugal pump makes it ideal for small room installations and other applications with confined floor space. The inline design of the pump’s inlet and outlets facilitates a smooth flow of the pumped liquid through the pump. Vertical inline centrifugal pump manufacturers avail the units in different designs such as singe-suction, double-suction, monoblock, rigidly coupled configuration, and spacer coupling design. Vertical inline centrifugal pumps primarily apply to transferring low-viscosity fluids such as water and some chemicals. They are perfect as circulator pumps in applications requiring water flow under high discharge pressure. Vertical inline centrifugal pumps present numerous advantages, including space-saving design, easier installation, increased energy efficiency, and reliability. However, the vertical inline centrifugal pumps require vertical clearance for installation and are pretty tricky to maintain.