Semi-submersible Pump
What is a semi-submersible pump?
A semi-submersible pump is a kind of pump in which the pumping element is immersed in the container with liquid, while the motor remains above the surface of the liquid. In terms of configuration, a semi-submersible pump is a vertical pump because of the vertical alignment of the operating shaft. The pump’s cylindrical casing is partially submerged in liquid and the shaft and the output spindle inside it are connected via a flexible coupling. A semi-submersible pump is usually bolted on a mounting plate which is fastened to the cover of the tank containing the pumping medium. The mounting plate is rigidly connected to the pump casing. However, small semi-submersible pumps may not contain a mounting plate. Semi-submersible pump manufacturers divide them into two categories based on the operating principle: rotor dynamic pumps (centrifugal pumps) and positive displacement pumps. Rotor dynamic semi-submersible pumps use a centrifugal or vortex wheel (i.e., impeller) while positive displacement semi-submersible pumps employ an eccentric screw or a piston to move fluid through the pump.

Figure: Showing the configuration of the semi-submersible pump
A semi-submersible pump is perfect for diverse uses such as draining full containers, basins, and barrels. It can excellently pump fluid from a large reservoir or a tank with a fixed depth. Additionally, the semi-submersible pump can also help to convey abrasive or corrosive products with low to high viscosity. They are easy to maintain and have low operating costs because the semi-submersible pump manufacturers design the pumps with a compact structure and distinctive features. Generally, a semi-submersible pump is a cost-effective alternative to other pump systems.
Components of a semi-submersible pump
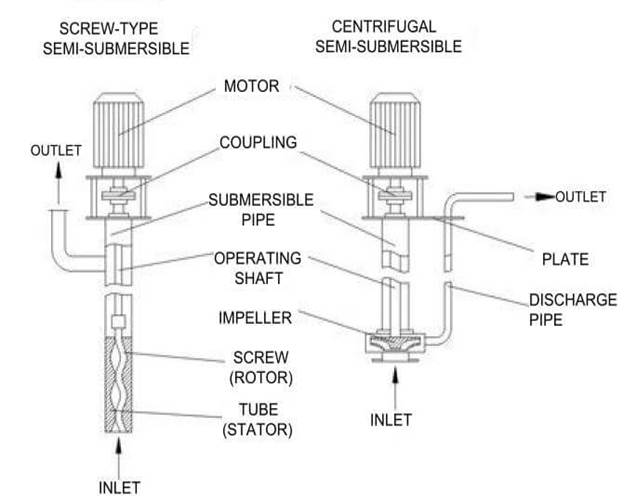
Motor
The electric motor is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy from the main electricity supply into mechanical energy. The electric motor is the prime mover of a semi-submersible pump, meaning that it provides all the mechanical power needed to run the pump. The motor shaft usually couples with the pump shaft to transmit toques. An electric motor can be either a DC motor or an AC motor, depending on the supply current. An Ac motor work with alternating current, while a Dc motor operates with a direct current.
Coupling
The coupling is the component connecting the motor to the operating element of the pump. The purpose of the coupling is to transmit drive torque from the motor shaft to the operating shaft. Couplings can be flexible or rigid type. A flexible coupling allows minor angular and parallel misalignment, while a rigid coupling requires precise shaft alignment, and any misalignment will negatively impact the pump’s performance and service life. A semi-submersible pump employs a flexible coupling between the motor shaft and the pump’s operating shaft.
Pump casing
The casing houses the shaft transmitting rotational motion from the motor to the operating element (screw or impeller). In a semi-submersible pump, the casing is usually vertical and bolted on the lower side of the mounting plate. During operation, the pump casing contains the liquid which enters through the inlet port and exits through the outlet port and delivery pipe. It is also sealed to prevent pump leakage and retain pressure. Semi-submersible pump manufacturers design them from a variety of materials that offer high strength, corrosion resistance, and casting capabilities. Such materials include iron, stainless steel, nickel and nickel base alloys, and plastics.
Rotor
The rotor or the pumping element of a semi-submersible pump can be an impeller (centrifugal pump) or screw (positive displacement pump). The function of the rotor is to increase the kinetic energy and pressure of the pumping fluid. The impeller contains a series of backward-curved vanes and can be either an open or closed impeller. Open impellers have only one shroud, and the vanes are exposed on one side and are mainly found in single-stage suction centrifugal pumps. A closed impeller has a cover on either side of the vanes. Both the open and closed impellers classify under a common category of impellers known as radial impellers, which displace fluid radially.
Operating shaft
The operating shaft is a rotary mechanical component riding on bearings and carrying the impeller. Its main purpose is to transmit the motor’s rotation motion to the pump rotor (impeller or screw), moving the fluid through the pump. Semi-submersible pump manufacturers design the shaft using solid metals such as stainless steel and carbon steel.
Discharge pipe
The discharge pipe is connected to the pump outlet port via flanges or pipe unions. Its function is to direct the pump discharge under pressure to the required location.
Inlet and outlet ports
The inlet port allows the fluid into the pump while the outlet port directs the pumped fluid out of the pump and to the required destination through the discharge pipe.
How does a semi-submersible pump work?
The operation of a semi-submersible pump is determined by the type of operating element in use. In a centrifugal semi-submersible pump, the motor rotates the impeller, creating a vacuum inside the pump due to the centrifugal effect of the impeller vanes. Since the atmospheric pressure outside the pump casing is greater than the pressure inside, the pumping fluid enters the pump casing. When the fluid strikes the impeller’s eye, the rotating blades impart great kinetic energy and velocity to the fluid while moving radially outwards into the volute chamber. Once in the volute chamber, the fluid flow velocity decreases while the pressure increases causing the fluid to exit the pump through the outlet port and discharge pipe to the desired location.
In the semi-submersible pump that employs a screw, the pump motor rotates the driver screw which then rotates the driven screw via a timing gear. As the screw rotates, they intermesh creating progressive cavities from the suction to the discharge side of the pump. These cavities trap and move the pumped medium from the suction inlet to the discharge outlet while compressing it to increase pressure.
Types of semi-submersible pump
The semi-submersible pump can be classified based on the particular application of the pump as follows:
Chemical semi-submersible pump
The chemical semi-submersible pump is used in the chemical industry for moving contaminated fluids with insoluble particles and fibers up to 6mm in size from their storage tank. It consists of gasket fits and a dry-running seal to keep vapors in the sump. Semi-submersible pump manufacturers may directly install the chemical pump on the surface of the pumped medium’s container. the chemical semi-submersible pump can handle liquid at temperatures of up to 105 degrees centigrade. It can also manage a pressure head of up to 80 meters and a maximum capacity of 16000 cubic meters per hour.
Figure: Showing a chemical semi-submersible pump.
Oil semi-submersible pump
This kind of semi-submersible pump is used for pumping lube oils for diesel engines in shipbuilding and stationary power stations.
Figure: Showing oil semi-submersible pump.
Drainage semi-submersible pump
A drainage semi-submersible pump applies in draining pits, deep roadway underpasses, and dewatering courtyards at high risk of flooding or groundwater. It is usually started automatically via float switches. It can handle unclean water with dirt and solids whose permissible particle size depends on the impeller design and pump size.
Figure: Diagram showing drainage semi-submersible pump.
Applications of semi-submersible pump
Semi-submersible pumps cover a significant scope of applications with uses in almost every industry due to the need to empty storage tanks or move liquids or viscous substances. They find applications in oil, chemical, water supply and disposal, pharmaceutical and food industries, etc.
- Semi-submersible pumps are used for cleaning and neutralization of hazardous substances and pollutants.
- They also apply in the evacuation of fluids from tanks and reservoirs of a fixed depth, as well as from drums and cisterns
- They are used for emptying chemicals and oils from storage containers.
- They are used for draining pits and dewatering country yards at risk of flooding.
- They are used to empty barrels and railway tanks.
Advantages of a semi-submersible pump
- A semi-submersible pump has a compact structure, eliminating long suction tube
- It does not require to be primed because the pumping element is usually submerged in water
- It requires less installation space as a major part of the pump is located inside the pump with only the motor fitted vertically above the surface.
- A semi-submersible pump is simple to repair and maintain as compared to a submersible pump because there is no need not to extract the entire pump.
- A semi-submersible pump doesn’t require complete sealing because the most vulnerable part of the pump (i.e., the motor) is located above the pumped medium. This significantly reduces the manufacturing complexity and the cost of the pump.
- It is highly efficient and reliable.
Disadvantages of a semi-submersible pump
- A semi-submersible pump requires vertical clearance for installation and maintenance.
- Semi-submersible pumps also do not fit all uses. They are mainly designed to deal with thin liquids like water or thick ones like sewage.
- The sharp turn on the discharge pipe may produce a significant loss in performance.
Troubleshooting a semi-submersible pump
The pump doesn’t start
- Blown fuse or tripped circuit breaker. Inspect and replace the fuse if it is necessary
- The voltage is irregular due to dirt or corrosion at the pressure switch. Inspect the pressure switch and clean it of any debris or pollution.
The pump gives out insufficient discharge
- The pump isn’t fully submerged. Make sure that the pump is fully immersed in the medium.
- The check valve has failed or is wrongly installed. Inspect the check valve, install it correctly or replace it
- The pump is operating in reverse. Check that the direction of the motor rotation matches the direction indicated by the semi-submersible pump manufacturer. Reverse the motor polarities.
- Clogged impeller. Inspect the impeller and clean it.
The overload protector keeps tripping
- The protector is in direct sunlight. Shade or ventilate the box
- Incorrect voltage. Inspect the line terminals to determine if the pump is getting the voltage designed by the pump manufacturer.
The pump’s operation is noisy
- The pump is working in cavitation. Check the alignment between the driver and the pump. Check that the suction line valves are fully open.
- Fluid viscosity is too high. Ensure that the pumped fluid’s viscosity is within the range specified by the semi-submersible pump manufacturer.
- The pumped fluid is mixed with air. Ensure the pump is fully submerged to prevent vortex formation on the fluid’s surface.
The pump is vibrating excessively
- Some pump components are unbalanced. Inspect and rebalance components if it is necessary.
- Oblique or unbalanced shaft. Inspect the shaft and replace or balance it as necessary.
- The impeller is severely worn out or defective. Inspect and replace the impeller with another one from the pump manufacturer if necessary.
- The motor is loosely fastened on the mounting plate. Tighten the motor. Ensure that tightening torque is as per the semi-submersible pump manufacturer’s standards.
Summary
A semi-submersible pump is a pump comprising a pumping element immersed in the pumped liquid and a motor installed on a mounting plate above the surface of the liquid. The motor shaft and the output spindle in a semi-submersible pump are connected via a flexible coupling. A semi-submersible pump is a vertical centrifugal pump because of the vertical alignment of the operating shaft. The semi-submersible pump can be split into two broad categories: rotor dynamic pumps, i.e., centrifugal pumps, and positive displacement pumps, depending on the principle of operation. Semi-submersible pump manufacturers also classify them as oil, drainage, and chemical semi-submersible pumps, according to the specific application of the pump. Semi-submersible pumps are excellent for a significant scope of applications in virtually all industries due to the growing need to empty tanks, reservoirs, drums, and cisterns. They have a compact structure and are easy to install and maintain. They are also comparatively cheaper than submersible pumps.



