Inline Booster Pump
Inline booster pumps play a crucial role in water systems, specifically designed to increase pressure and flow rates. Whether for domestic use or industrial applications, understanding the types, applications, and troubleshooting aspects is essential for efficient operation.
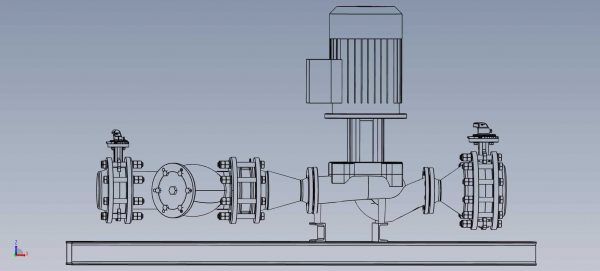
Types of inline booster pump
Inline booster pumps come in two main types based on the orientation of the pump shaft: vertical and horizontal.
Vertical Inline Booster Pump
The vertically oriented pump shaft of this type is suitable for high-temperature and high-pressure liquids. It’s ideal for confined spaces due to its small footprint. However, it may face challenges with high suction pressure and is not suitable for handling liquids with high concentrations of dissolved gases.

figure: vehicle inline booster pump
Horizontal Inline Booster Pump
Featuring a horizontally oriented shaft, the horizontal inline booster pump is efficient even with high suction pressure. It’s easy to maintain, making components easily accessible. While it takes up more floor space, it is suitable for various applications and can be coupled with different prime movers.

Figure: horizontal inline booster pump
Components of an inline booster pump
Regardless of the type and inline booster pump manufacturer, an inline booster pump consists of several key components:
- Motor: Powers the pump impeller to run the pump.
- Impeller: Moves fluid from the inlet to the outlet.
- Inlet and Outlet: Connects to the waterline and household water distribution piping.
- Pressure or Flow Sensing Sensor: Measures fluid pressure and flow rate for adjustments.
Working principle of inline booster pump
An inline booster pump connects directly to the main water line or pressure tank, supplying enough water pressure to move it to the desired location. The impeller, powered by an electric motor, imparts high kinetic energy to the water, converting it into high-pressure head before leaving the pump casing.
Characteristics of inline booster pump
Inline booster pumps offer several desirable characteristics:
- Directly coupled to an electric motor.
- High efficiency.
- Compact structure with a small volume.
- Easy to install and maintain with a pull-out design for accessing internal components.
- Horizontal configuration suitable for indoor applications with low headroom requirements.
Applications of inline booster pump
Inline booster pump finds application in many kinds of water engineering scenarios, including:
- Constant pressure water supply systems
- Circular booster of cold and hot water in bathrooms
- Iron and steel metallurgy
- Air condition systems; district heating/cooling, drainage of central heating system
- Heater circulatory system
- Farmland irrigation and drainage
- Support of firefighting equipment; firewater pumps
- Industrial transfer of corrosive medium without suspended grain or medium.
- Pumping non-flammable or non-explosive liquid without grain or fiber
- Power plant water supply and drainage
Advantages and Disadvantages of Inline Booster Pump Advantages:
Advantages:
- Simple and compact design, requiring relatively small installation space.
- Low initial installation and maintenance costs.
- High reliability and efficiency.
- Energy-efficient as they operate only when needed.
Disadvantages:
- Requires strong piping to handle high water pressure.
- Adds to electricity costs.
- Mechanical seal problems due to gas accumulation.
- Potential corrosion issues with non-stainless pumps.
Selection of an inline booster pump
Choosing the right inline booster pump depends on several factors:
- Distance from the water source.
- Elevation of the water storage tank.
- Desired flow rate.
- Desired fluid pressure.
- Location of the water source.
Troubleshooting inline booster pump
Address common issues with the inline booster pump:
- Pump not starting or running.
- Motor overheating and shutting off.
- Excessive vibrations.
- Pump driver overloaded.
- Bearings overheating.
Summary
In summary, an inline booster pump is a vital component for high-pressure flow applications, offering advantages in efficiency, compact design, and reliability. Understanding its types, applications, and troubleshooting aspects is crucial for optimizing its performance in various scenarios.
