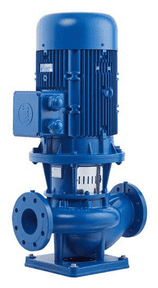
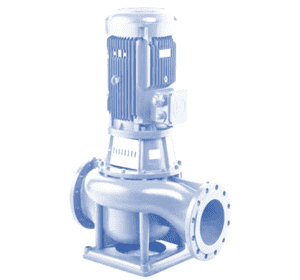
Vertical Inline Centrifugal Monoblock Pump
What is a vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump?
A vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump is an electric drive pump with a single shaft connecting the motor to the pump head, mainly in a vertical arrangement. The motor bearings carry the full rotary load of the shaft during pump operation. The pump’s suction and discharge ports lie straight to the piping system; hence the term inline is used in naming the pump. The inline design facilitates a smooth flow of the pumped liquid through the pump system. The vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturers develop the units to fit light-duty applications and applications with short operation periods at full motor speed. The vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump is ideal for transporting low-viscosity fluids, including water and some chemicals. It can be suspended along a pipeline like a valve to boost pressure. Its vertical design is space-saving and suitable for installation in confined spaces. Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps can manage a wide range of flow rates and high-pressure heads.

Figure: Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump
Components of vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump
Motor
The motor acts as the pump’s prime mover, providing the mechanical power to run the pump. The vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump uses an AC electric induction motor which in most cases is close-coupled to the pump body.
Pump casing
The pump casing contains the pump’s internal components and acts as a pressure containment vessel. It is usually made from cast steel or cast iron and sealed to prevent leakage. The pump casing also carries the diffusing chamber that helps convert the fluid’s kinetic energy to the pressure head and guides the pumped liquid to the outlet.
Shaft
The shaft is a rotary cylindrical component centrally located in the pump and supported on bearings. Its primary function is to carry the impeller. Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturers design the pump shaft from solid and corrosion-resistant materials, such as stainless steel, bronze, etc., to ensure long service life.
Impeller
The purpose of the impeller is to impart kinetic energy to the pumped liquid and displace it through the pump body. Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturers create the impeller using various materials such as cast steel, ductile cast iron, and alloy steel. The vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturers mainly fit the units with a closed-type impeller to provide high efficiency and high-pressure head. A closed impeller can have either single-suction or double-suction designs.
Figure: Single suction impeller.
Figure: Double suction impeller.

Figure: Single suction impeller

Figure: Double suction impeller
How does a vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump work?
A vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump operates on the principle of the forced vortex. This principle states that when a mass of fluid rotates due to an external force, its pressure head rises, leading to fluid transfer from one location to another. When the electric motor starts, the impeller rotates with the liquid inside the pump, creating a vacuum in the impeller’s eye. As a result, water flows into the pump casing and towards the impeller’s eye to fill the void. Once the water strikes the impeller, the centrifugal force acting on the vanes rotates it radially and axially outwards until it passes through all of the impeller components and enters the diffuser at a very high velocity. In the diffusing chamber, the water speed gradually decreases because of the enlarging progressively flow path, and the extreme fluid velocity converts into a high-pressure head. The water then discharges through the pump outlet and enters the piping network to be moved to the required destination.
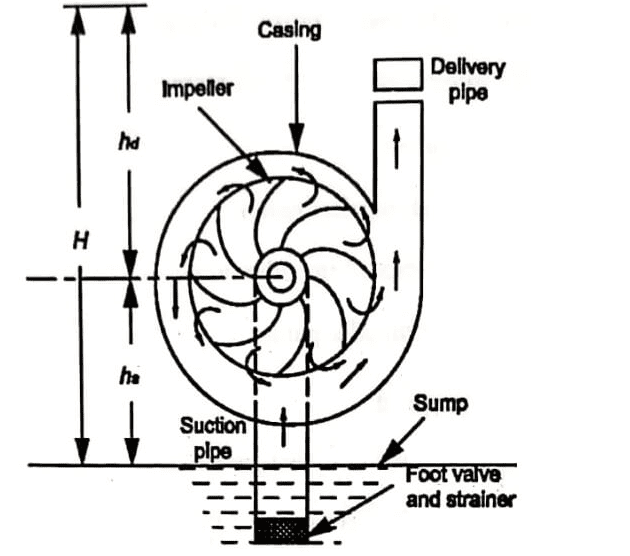
Figure: Working of a vertical inline centrifugal Monoblock pump
Types of vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps
Single-suction vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump
In a single-suction vertical centrifugal monoblock pump, the pumped liquid enters from one side of the pump impeller and exits from the other side. This pump is compact in construction and provides smooth operation.
Figure: Single-suction vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump
Double-suction vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump
The double-suction vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump consists of a double-suction impeller (also called a double inlet impeller). The double suction impeller features two back-to-back impellers, allowing the pumped liquid to enter from either side and discharge from the middle section. The double-suction vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps can achieve a higher flow rate than their single-suction counterpart. Because of the double-suction impeller, the flow at the pump inlet is also comparatively low; hence the double-suction vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump operation is cavitation free.
Figure: Double-suction vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump
Applications of vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps
Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps cater to a broad scope of industrial, civil, and commercial applications, including agricultural irrigation, water supply to buildings, civil schemes, and pipelines. They also constitute essential components in various industrial systems, including hydrants, firefighting, air conditioning, and hot water systems. Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps are used to do the following:
- Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps are used to transport water for various uses in homes and industries.
- They apply as booster pumps in water supply systems and other systems where pumped liquid needs to be pressurized.
- They are used to support firefighting equipment.
- They are used to supply and circulate water in hot water heating systems.
- They are used for irrigation in agricultural farms.
- They are used along with air conditioning systems air commercial buildings.
- They are used in cleaning and industrial recirculation system.
- They also apply to transport water in municipal works and wastewater treatment.
Advantages of a vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump
- Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps do not require extra base plates or coupling for fitting.
- They have high energy efficiency because they rely on gravity-fed flow.
- They are high reliability in operation.
- Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps have a small overall size with less complexity during installation.
- The monoblock design eliminates the need for coupling and shaft alignment, hence easier pump installation and servicing.
- Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps present a quiet and low-vibration operation because the vertical shaft is naturally balanced, and the gravitation force does not act against the direction of shaft rotation.
- They have high efficiency and can tolerate higher temperatures and pressure.
- Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps have higher Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) than suction pumps.
- They are self-supporting and cost-effective.
Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps require a small space for installation because the motor and service clearance sit above the pump casing.
Disadvantages of a vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump
- Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps require more headroom for installation and maintenance.
- It can be challenging to repair the internal components because a standard shaft motor cannot apply, and sourcing must be from the original vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturers.
- Seal leakage may occur above the pump casing leading to corrosion.
- Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps may experience mechanical seal problems.
The mechanical seals may dry out or fail due to infiltration and accumulation of gases in the seal chamber. Leakage in the mechanical seals can damage the motor.
- Pumps with large motors above 25 hp can be challenging to maintain because the maintenance personnel must disconnect the prime mover and the impeller from the volute to service the mechanical seals.
Troubleshooting a vertical Inline centrifugal monoblock pump
The pump won’t start
- There is a blown-out fuse or tripped circuit breaker. Inspect the vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump for a blown-out fuse and replace it if necessary.
- The power supply to the panel is insufficient. Ensure that the motor receives the right amount of voltage and current.
The pump driver is overloaded
- There is mechanical friction within the pump. Inspect the pump assembly for any obstruction or deflection.
- Wrong voltage supply. Check that the pump receives the proper voltage following the vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturer.
- The pump’s speed is too high. Lower the pump speed.
- The density and viscosity of the liquid exceed the pump design. Ensure that the vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump suits the particular application.
Zero discharge after startup
- The inline pump operation is reversed. Check that the direction of the motor rotation matches the direction of the vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturer’s arrow indicated on the pump casing. Reverse the motor polarities.
- There is air in the pump or suction pipework. Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps cannot prime with air on the suction side. Ensure that the pump or pipework is filled with water to drive out the air from the pump system.
- The check valve is fitted incorrectly. Install the check valve properly or replace it.
- The pump’s monomeric head is insufficient due to high friction losses exceeding the pump design. Be sure to raise the pump power to the level recommended by the vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturers. Open all the valves and ensure the delivery pipes are of the correct sizes.
- The pump inlet is blocked. Clear the channel of any obstruction.
- The impeller or check valves are clogged. Clear any blockage from the impeller and the valves.
The noise level is too high
- The rotating part rubs on the stationary component. Dismantle the pump and correct the rotor assembly.
- Some pump components are excessively worn-out. Inspect the rotor assembly for worn-out bearings or impellers and replace them if necessary.
- The pump is working outside the duty range. Ensure the correct duty range according to the vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturer’s manual.
- The pump is working in cavitation. Ensure that the net suction pressure head meets the vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturer’s specifications. Be sure to open the suction line valves fully.
- Some pump parts are loose. Tighten the components to the torque level recommended by the vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturers.
The pump is vibrating excessively
- There are unbalanced components in the pump. Inspect and rebalance the vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump components as necessary.
- The impeller is severely worn-out. Inspect and replace the impeller with another one from the vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturer if you find it fit.
- The pump shaft is oblique or unbalanced. Inspect the post, rebalance it as required, or replace it.
- The shaft is bent. Dismantle and replace the shaft if necessary.
- There is excessive thrust due to mechanical failure. Inspect the pump assembly and correct any shortcomings.
Bearings have a short life
- Excessive cooling of water-cooled bearing, resulting in condensation of atmospheric moisture in bearing housing. Reduce the flow of cooling water.
- The shaft is bent. Inspect and replace the shaft if necessary.
- There is rusting of bearings from water in the housing. Inspect for water ingress avenues and seal them.
- The bearings are worn-out due to the shaft running out. Replace them if necessary.
- The rotating components are rubbing against the stationary part. Correct the assembly.
Summary
A vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump is an electric drive pump consisting of a single shaft connecting the motor to the pump head. The pump’s motor is close-coupled to the pump head, usually in a vertical installation. In addition, the suction and discharge ports lie straight to the piping system. The motor bearings stand the full rotary load of the shaft during pump operation. The inline design facilitates a smooth flow of the pumped liquid through the pump system. Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps are ideal for transporting low-viscosity fluids, including water and some chemicals. They are extensively used in various industrial, civil, and commercial applications, including agricultural irrigation, pipelines, building water supply, and civil schemes. Vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pumps have many advantages, including space-saving design, less complex installation, excellent energy efficiency, and reliability. However, repairing the pump’s internal components is challenging because a standard shaft motor cannot apply, and sourcing must be from the original vertical inline centrifugal monoblock pump manufacturers.