Pneumatic Diaphragm Pump
What is a pneumatic diaphragm pump?
The pneumatic diaphragm pump is a positive displacement pump that uses compressed air to move liquids by use of a reciprocating force and either a ball valve or flapper valve. The name of this pump comes from a diaphragm membrane used to do the pumping action. This diaphragm works on the principle of air displacement. The diaphragm is pushed and pulled into and out of the pumping chamber to allow fluid flow. This type of pump is very versatile as it can transport liquids with high, low, and medium viscosities as well as fluids with suspended particles. Pneumatic diaphragm pump manufacturers design this pump for use even in aggressive chemicals like acids as they can be constructed with various types of materials and diaphragms resistant to corrosives., This pump can be used in handling a wide variety of fluids in various industries such as water supply, mining, chemicals, oil and gas, paper, and pulp among others.

Figure: Pneumatic diaphragm pump
Components of a pneumatic diaphragm pump
Motor
The motor is used to provide the power that operates the pneumatic system to produce compressed air. The power from the motor is transmitted using a shaft. The shaft then operates a piston to produce compressed air. The piston is mounted at the central part of the diaphragm which causes it to oscillate as it moves fluid from suction to discharge end.
Driveshaft
This is a shaft that transmits energy from the motor to the pump’s connecting the rod and crank.
Connecting rod and crank
The connecting rod and crank are used to convert rotational motion into oscillatory motion. The connecting rod connects the motor shaft to the piston.
Diaphragm
This is a component made of rubber or thermoplastic material and is mounted over the piston. The diaphragm is meant to expand and collapse the fluid volume of the pumping chamber to ensure the pump can operate. The diaphragm is also tasked to separate the transmission and pumping parts and prevent the fluid from getting into the other parts of the pump. Pneumatic diaphragm pump manufacturers consider various factors when designing the diaphragm to ensure the pump has long service life depending on where it will be used.
Suction and delivery valves
The suction valve is used to control fluid flow into the pump and also prevent any attempt of the fluid from flowing backward. The discharge valve controls fluid flow from the pump and prevents any fluid from returning to the pump.
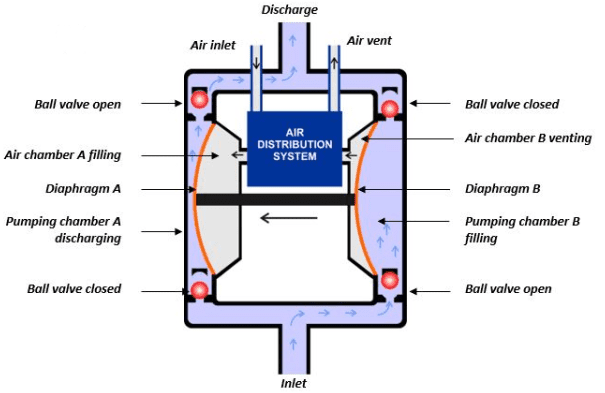
Figure: Components of a pneumatic diaphragm pump
How does a pneumatic diaphragm pump work?
This pump operates by the use of two flexible diaphragms. The diaphragms move forward and backward to create a temporary vacuum. This vacuum is meant to move the liquid into the pump. The diaphragm membranes act as partitions between the liquid and air. The working of this pump involves two strokes. In the first stroke, the diaphragms are connected through a shaft via the central part where the air valve is placed. This valve is used to move compressed air behind the first diaphragm and force it away from the middle part. As such, the first diaphragm produces a pressure stroke that transports fluid from the pump. At the same time, the second diaphragm suctioning process.
The air behind the second diaphragm is freed into the atmosphere and the atmospheric pressure moves the fluid into the suction side. In the second stroke, the outlet valve is pushed out of its seat. When the second stroke is completed, the air valve moves the air behind the first diaphragm and the whole cycle repeats.
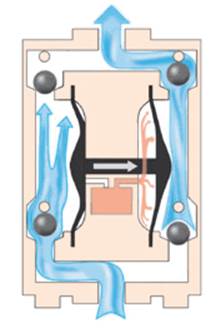
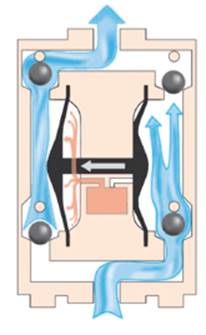
Figure: Working of a pneumatic diaphragm pump
Types of pneumatic diaphragm pump
Engineering plastic pneumatic diaphragm pump
This is a pump that is made of engineering plastic material. This material has better thermal and mechanical properties compared to commonly used plastics such as PVC and polystyrene. However, a pump made of this material is quite expensive relative to those made of common plastics like PVC. The operating temperature of this pump is somehow higher than that of the plastic pump because the engineering materials have higher thermal resistance relative to the plastics.
Aluminum pneumatic diaphragm pump
This is a pump made of aluminum material. This type of pump is preferred for lightweight and high strength and resistance to high temperatures which makes it reliable and safe to operate. The high strength of the aluminum allows this pump to produce fluid flow at high pressure suitable for long-distance transportation. Aluminum also has other advantages such as being non-toxic and having excellent corrosion resistance making it suitable for use in corrosive fluids. Due to the aluminum material, the pump is easy to machine and produce due to the malleability of aluminum material. However, this pump is expensive relative to the engineering plastics pump.
Stainless steel pneumatic diaphragm pump
This is a pneumatic diaphragm pump made of stainless steel material. This pump is very strong relative to pumps made of engineering plastics and aluminum. As such, this pump is suitable for use where high pressure is needed. Stainless steel is also resistant to corrosion and has low thermal expansion suitable for high temperatures. However, this pump is heavier compared to engineering plastic and aluminum pump.
Factors to consider when selecting a pneumatic diaphragm pump
Volume requirements
It is important to select the pump such that it will operate at 50% of its highest potential during normal use. If operated at 50% of its highest potential, it will be able to operate for long periods without maintenance. Pneumatic diaphragm pump manufacturers design this pump with their working capacity in gallons per minute on the manual. This would help to select a pump best for 50% fluid capacity.
Pump material
Pneumatic diaphragm pump manufacturers produce these pumps from different materials. One of the key component materials to consider are the ball, pump seat materials and the pump body materials. The choice of coating material used determines the type of fluid the pump can be used to operate on. It also dictates the operating temperature and choice of solids contained in the fluid. For example, stainless steel material is resistant to corrosion and wear but it is expensive. Plastic material like PTFE is resistant to corrosion and has low cost but it is not resistant to abrasive wear.
Pump performance curve
Pneumatic diaphragm pump manufacturers design each pump with a specific performance curve. This curve shows how the pump would perform at a certain pressure head and flow rate as well as the amount of air needed at various levels of operation. This helps to know if the pump being considered will be able to deliver the required fluid load.
Applications of pneumatic diaphragm pumps
- Mining. These pumps are used in dewatering below and above-ground sites and quarries, transporting sludge and slurries and transporting fuel for heavy construction and or vehicles.
- Chemical processing plants. Pneumatic diaphragm pumps are used in loading and unloading processes, as portable utility pumps, dosing, or batching chemicals.
- Ceramics. It is used in ceramic slips, filling molds, and day tank transfer.
- Coatings. The pneumatic diaphragm pump is used to transport, dispense and dose ink or paint, for spray guns.
- Electroplating and anodizing. It is used to replenish chemicals in metal finishing tanks or plating, filtration, and agitation of cleaning solutions.
- Pulp and paper industries. It is used to transport glues, printing inks, and bulk adhesives.
- Water and water treatment. Pneumatic diaphragm pumps are used in the transportation of domestic and commercial water as well as suspended media such as wastewater.
- Oil and gas. It is used in a filter press, settling pond transfer, and bulk fuel transfer.
Advantages of pneumatic diaphragm pumps
- These pumps are oil-free and they have fewer seals, unlike centrifugal pumps.
- It has excellent wear resistance making it suitable for use in abrasives.
- It can prime itself for a head of around 6 m.
- Pneumatic diaphragm pumps have large fluid displacement volumes.
- It has a simple and compact design.
- It is easy to clean and repair.
- It is of high versatility as it can work in almost all industries except those involving very temperatures.
- This pump can transfer toxic, abrasive, and corrosive fluids.
- Pneumatic diaphragm pumps can transport highly viscous fluids such as grease and tar.
- These pumps have less wear on the diaphragm relative to mechanically driven diaphragm pumps due to pressure balance by the compressed air.
- The design of these pumps helps to separate the liquid and sensitive parts of the pump and thus reduces the chances of repair.
Disadvantages of pneumatic diaphragm pumps
- These pumps have low operating speeds.
- Its energy efficiency is quite low relative to other pumps.
- Pneumatic diaphragm pumps are not suitable for use at high temperatures.
- They do not produce high pressure relative to centrifugal pumps.
Troubleshooting pneumatic diaphragm pumps
The pump does not start
- Broken diaphragm. Replace the diaphragm.
- Low air flow rate. Check pipe connections, size, and pump consumption relative to other devices connected on the same line.
- Low air pressure. Adjust pressure level. Also, check pump consumption against other devices mounted on the same line.
- Lack of air. Ensure valves, air circuits and connections are well functioning.
- The control valve is damaged. Replace the control valve.
- The suction valve is closed. Open the suction valve.
- The discharge valve closed. Open the discharge valve.
- The pneumatic exchanger is damaged. Replace the exchanger.
- The pump has stalled. Reset the pump according to the pneumatic diaphragm pump manufacturer.
The pump does not deliver any fluid
- The valve ball not seating correctly. Disassemble the ball valve according to the instructions given by the pneumatic diaphragm pump manufacturer and clean the valve seat and ball or replace them if necessary.
- Too high suction lift. Reduce the suction lift.
- Too high fluid viscosity. Increase intake pipe diameter and reduce pump cycles.
- Blocked suction pipe. Open the pump and remove any blocking material.
Pump cycles reduce
- The suction pipe is blocked. Check the suction pipe and remove any blocking material.
- Highly viscous fluid. Increase pipe diameter or use a larger pump. Ensure the pump is used for the fluid viscosity recommended by the pneumatic diaphragm pump manufacturer.
- Delivery pipe blocked. Clean off blocking materials.
Low fluid flow rate
- Highly viscous fluid. Use large-diameter pipes, use a large-sized pump, and run the pump at a slow speed.
- The intake pipe is not connected correctly. Connect the pipe properly.
Summary
A pneumatic diaphragm pump is a positive displacement pump that operates by use of compressed air. As the name suggests, this pump uses a diaphragm component made of materials such as Teflon, rubber, or thermoplastic to create a reciprocating motion that helps to move the liquid. Pneumatic diaphragm pump manufacturers design this pump to use two flexible diaphragms that are mounted on a shared shaft to move forward and back repeatedly as they pump the fluid into and out of the pump chamber. This type of motion creates a vacuum in the pump which helps to intake fluid via an inlet port.
Pneumatic diaphragm pump manufacturers produce various types of pumps based on different materials such as engineering plastics pumps, stainless steel pumps, and aluminum pumps among others. Applications of these pumps include mining, water supply, wastewater treatment, oil, and gas, paper and pulp, chemical processing, and powder coating among others. The advantages of these pumps are wear resistance, corrosion resistance, easy cleaning, and repair, versatility, self-priming, and large fluid displacement.
