Deep Well Submersible Pump
What is a deep well submersible pump?
A deep well submersible pump is a long cylinder-shaped device located underwater, deep into the well as its name implies, and helps push the water to an above-ground reservoir. The pressure of the surrounding water eases the movement of the water through the pump. Deep well submersible pump manufacturers fit the unit with high starting torque motors to help loosen mineral deposits that may adhere to the pump’s moving parts. Deep well submersible pumps can be used in almost any well, regardless of how deep or shallow it is. When the motor turns on, water is drawn into the pump, which pushes it to the surface and into a storage tank, where it will be stored until needed. Deep well submersible pumps are suitable for pumping clean water for many applications such as domestic supply, irrigation, and water systems for small communities. Deep well submersible pumps are waterproof, long-lasting, self-priming, energy-efficient, cavitation free, and require little maintenance.

Figure: showing the configuration of a deep well submersible pump
Components of a deep well submersible pump
Electric motor
Deep well submersible pump can work with either single phase (230V) or three-phase motor (400V). The electric motor provides the mechanical power to run the pump. It is hermetically sealed and close-couped to the pump body. Deep well submersible manufacturers also integrate the electric motor with a protection device to shut down the pump in case any hitch occurs.
Electrical cable
The purpose of the electrical cable is to deliver power to the deep well submersible pump. The electrical cables can be two or three power cables depending on the motor design.
Pump casing
The casing is the outside shell of the pump, which is sealed to retain pressure and protect against fluid leakage. It contains the pump’s internal components, helps to convert the kinetic energy into a pressure head, and guides the water in and out of the pump. The pump casing can be made from various materials, including cast iron, cast steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc.
Shaft
The shaft is a rotary stainless or carbon steel solid, riding on bearings and carrying the impeller. Deep well submersible water pump manufacturers create the shaft to resist the heavy loads and vibrations during pump operations.
Bearings
The primary purpose of the bearings is to support the rotor and the shaft and to align them correctly with the fixed ends under the action of radial and axial forces. Additionally, they reduce the friction between the rotating shaft and the stator and contain the relative motion of the rotor assembly.
Impeller
The impeller consists of an arrangement of backward-curved vanes and rides on the electric motor’s shaft. Its primary function is to displace fluid through the pump by increasing its kinetic energy and pressure. The impellers differentiate themselves in design and can be open, semi-open, or closed.
Valves
The deep well submersible pump is also fitted with different types of valves to help with the pumping operation. Such valves include relief valves, drain valves, and ball valves.
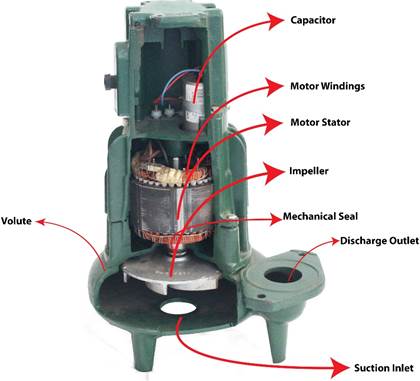
Figure: Components of a submersible deep well pump
How does a submersible deep well pump work?
The deep well submersible pump pushes water up through a pipe connecting to one end of the pump. The pump converts energy from electrical into mechanical and then kinetic and pressure energy of the fluid. When the motor starts, the pump impeller rotates the water pre-filled in the pump casing, imparting high kinetic energy and velocity to the liquid. The impeller then throws the water into the volute, where the fluid speed decreases due to the gradually enlarging flow path as the high fluid velocity converts into high static pressure. Finally, the water exits the pump under elevated pressure, which helps to push it to the surface and to direct the flow to the designated location via the delivery connections.
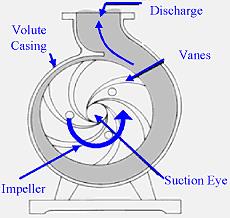
Figure: Working of a deep well submersible pumps
Types of deep well submersible pumps
Stainless-steel deep well submersible pump
The stainless-steel deep well submersible pump is made up of a 304 stainless-steel construction to resist rust and corrosion in underwater conditions excellently. The deep well submersible pump manufacturers fit the device with a built-in check valve to enhance its suitability for home and industrial applications. The stainless steel deep well submersible pump can provide a large head of up to 164 feet and a maximum flow rate of 25 gallons per minute.
Figure: Stainless-steel deep well submersible pump.
Single-stage deep well submersible pump
A single-stage deep well submersible pump is made up of one impeller rotating on a shaft in a pump chamber, designed to pressurize and push the liquid to the surface when powered using a motor. This pump offers the most uncomplicated design of the deep well submersible pump. It is, therefore, less costly and easy to acquire.
Figure: Single-stage deep well submersible pump.
Multistage deep well submersible pump
The multistage deep well submersible pump has more than two impellers supported on a single shaft and located in different pump chambers mounted in series. Every single chamber and impeller assembly constitutes a pump stage. This pump draws water into the first pump stage at suction pressure and exits from the last stage at elevated pressure. The multistage deep well submersible pump can generate greater power and static pressure using a smaller motor, thereby consuming less energy. It also can provide higher water pressure and flow rates compared to the single-stage counterpart.
Figure: Multistage deep well submersible pump.
Applications of deep well submersible pumps
Deep well submersible pumps are widely used to pump clean water from deep wells for domestic, civil, and industrial purposes. They are primarily found in farmland, factories, railways, mines, water supply systems, and pressure systems. They are also used in rivers, reservoirs, canals, and other water-lifting works. Their typical uses include the following:
- Deep-well submersible pumps are used for lifting water from a deep underground well into surface storage tanks or treatment facilities.
- They are used for domestic and irrigation water supply.
- They are used for pumping tasks in municipal engineering
- They are used for dewatering mines.
- They are used with home faucets to ensure a steady water supply to the house and tanks.
Advantages of a deep well submersible pump
- Submersible deep well pumps are highly versatile in application.
- They have minimal maintenance requirements.
- They can handle water with a sand content of up to 150 g/m3 because the deep well pump manufacturers construct them with floating impellers.
- They are cavitation free since they eliminate the spike in pressure as the water flows through the pump.
- Pumps are more effective for deep wells and go down several hundred feet compared to jet pumps.
- They provide an extended service life.
- They have a robust design that is easy to operate and install.
- Pumps provide a constant supply of water even during dry seasons.
- They don’t require priming since they are submerged in water.
- They provide consistent water pressure.
- They can move water over long distances.
- They are energy-saving due to reduced energy consumption. They also take advantage of gravity in the pumping process; hence they do not consume energy to draw water into the pump.
Disadvantages of a deep well submersible pump
- Deep well submersible pumps are more complex to design, therefore, more expensive than surface pumps.
- They are unfit for abrasive liquids and water containing heavy scales.
- It isn’t easy to repair the pump. Pump repairs involve the removal of the pump from the well to the surface, which may raise repair expenses.
- The pump seals may corrode over an extended duration of pump operation, causing pump leakage.
- Since the motor is hermetically sealed, it is often challenging to disassemble and repair it.
Troubleshooting a deep well submersible pump
The motor won’t run
- There is no power supply to the Control Panel. Use a voltmeter across the input terminal to confirm the voltage supply to the panel. Ensure the power cable connections are consistent with the deep well submersible pump manufacturer’s standards.
- There is heavy sedimentation around the deep well submersible pump. Inspect the pump and remove any build-up.
- There is a broken power cable in the deep well submersible pump. Inspect, repair, or replace any power cable.
- There is a tripped circuit breaker or blown-out fuse. Reset the circuit breaker if necessary. Inspect the pump for a blown-out fuse and replace it.
- There are shortcomings in the motor wiring. Consult a licensed deep-well submersible pump dealer to inspect the wiring connection and correct any faults.
The pump gives zero discharge
- The sediment filter is blocked. Inspect and clean the sediment filter.
- The discharge pipe is blocked. Inspect and clean the discharge pipe.
- The pump’s discharge head is insufficient. Ensure there is no obstruction or leakage in pipes. Ensure that the pump’s discharge head matches the system design values specified by the deep well submersible pump manufacturer.
- The pump is operating in reverse. Be sure to reverse the motor polarities. Check that the motor rotation direction is in line with the direction shown by the arrow on the deep well submersible pump nameplate.
- The impeller is clogged. Inspect and clean any clogging material from the impeller.
Thermal trip
- The diver is overloaded. Make sure the pump draws the right amount of current and voltage.
- The pump head is too low. Adjust the pump head or install a control valve to detect back pressure according to the set value.
- The stop level is too low. Verify the stop switch level from the deep well submersible pump manufacturer’s manual and adjust accordingly.
Low pump flow rate
- The pump’s motor is rotating in reverse. Be sure to reverse the motor polarities.
- There is excessive clearance leading to fluid recirculation. Ensure that the deep well submersible pump use impellers of the correct sizes.
- The impeller is severely worn-out. Inspect the impeller for wear and replace it if necessary.
- The suction is clogged. Clean any closing material from the suction line.
- The discharge pipe is blocked. Inspect and clear any blockage from the discharge pipe.
The pump is overheating
- The pump is not fully submerged in operation. Check and fully submerge the pump if necessary.
- The thermostat is set too high. Set the thermostat to the temperature level specified by the deep well submersible pump manufacturers.
- There is heavy organic or mineral material built up around the pump. Inspect and clean any build-up from the pump.
- The cooling system provides an insufficient cooling water flow rate. Ensure that the cooling system is working correctly and without leakage.
The leakage detector is activated
- The detector cable is compromised due to wear or contact with oils. Inspect the detector cable and replace it if necessary. Rewind the motor if water ingress takes place.
Summary
A deep well submersible pump is a long cylinder-shaped device located deep into the well to help push the water to an above-ground reservoir. Deep well submersible pump manufacturers fit the edge-cutting unit with a high starting torque motor to help loosen mineral deposits that may adhere to the pump’s moving parts. They are available with single-phase or three-phase motors and in single-stage and multistage configurations. Deep well pumps can be constructed from various materials, including cast iron, cast steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc. Deep well submersible pumps are perfect for any well, whether deep or shallow. They are widely used to pump clean water from deep wells for domestic, civil, and industrial purposes. Deep well submersible pumps are energy-saving because they take advantage of gravity and the surrounding water pressure to help with the pumping process. They also can handle water with a significant amount of sand content (150 g/m3) because the deep well pump manufacturers construct them with floating impellers.



